The term "autoimmune diseases" refers to a broad category of illnesses that can affect virtually any region of the body and cause a variety of symptoms and problems.
This complicated group of illnesses affects almost 50 million Americans and those across the globe. Under these circumstances, healthy cells and tissues are unintentionally targeted and attacked by the immune system of the body, which is meant to defend us against dangerous invaders like viruses and bacteria.
This can impact practically every part of the body and causes a wide range of symptoms. Chronic, life-altering, and occasionally even life-threatening autoimmune illnesses are extremely likely.
There are nearly 80 autoimmune diseases out there and while it is impossible to be well-accustomed to each, it is important to be aware of them.
What is an Autoimmune Disease?
Your immune system, when functioning normally, is known to maintain your health because it can usually distinguish between foreign and your own cells.
However, when you have an autoimmune disease, your skin or joints are mistakenly perceived by your immune system as alien invaders. Autoantibodies, which are proteins released by it, target healthy cells.
While attempting to defend your body against actual threats, such as viruses and bacteria, immune system overreacts and fights itself instead, resulting in painful and sometimes dangerous symptoms that lower your quality of life.
Although they can affect men as well, autoimmune illnesses are known to affect women more frequently than men. One can adopt different measures to strengthen the immune system.
Common Causes of Autoimmune Diseases

While the actual cause of autoimmune diseases may be unclear, there are several factors that impact it -
- Your sex
- Family history and genetics
- Environmental factors such as exposure to the sun or mercury
- Your diet and nutrition
- Prior health conditions such as obesity
Common Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Low grade fever
- Swelling
- Skin rashes
- Numbness
Make sure to get evaluated by your primary care doctor if you identify with several of the symptoms.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Commonly known as RA, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that mostly affects the joints. It is characterized by persistent pain, stiffness, and inflammation, which, if left untreated, can frequently result in joint deformity and disability.
When the immune system unintentionally targets the synovium—the lining of the membranes surrounding the joints—it can lead to rheumatoid arthritis. This causes inflammation and eventually erodes the bone and cartilage in the joints.
While it tends to appear in the later stages of life, for some people it can start in their 30s as well.
Symptoms of RA can vary in severity and may include:
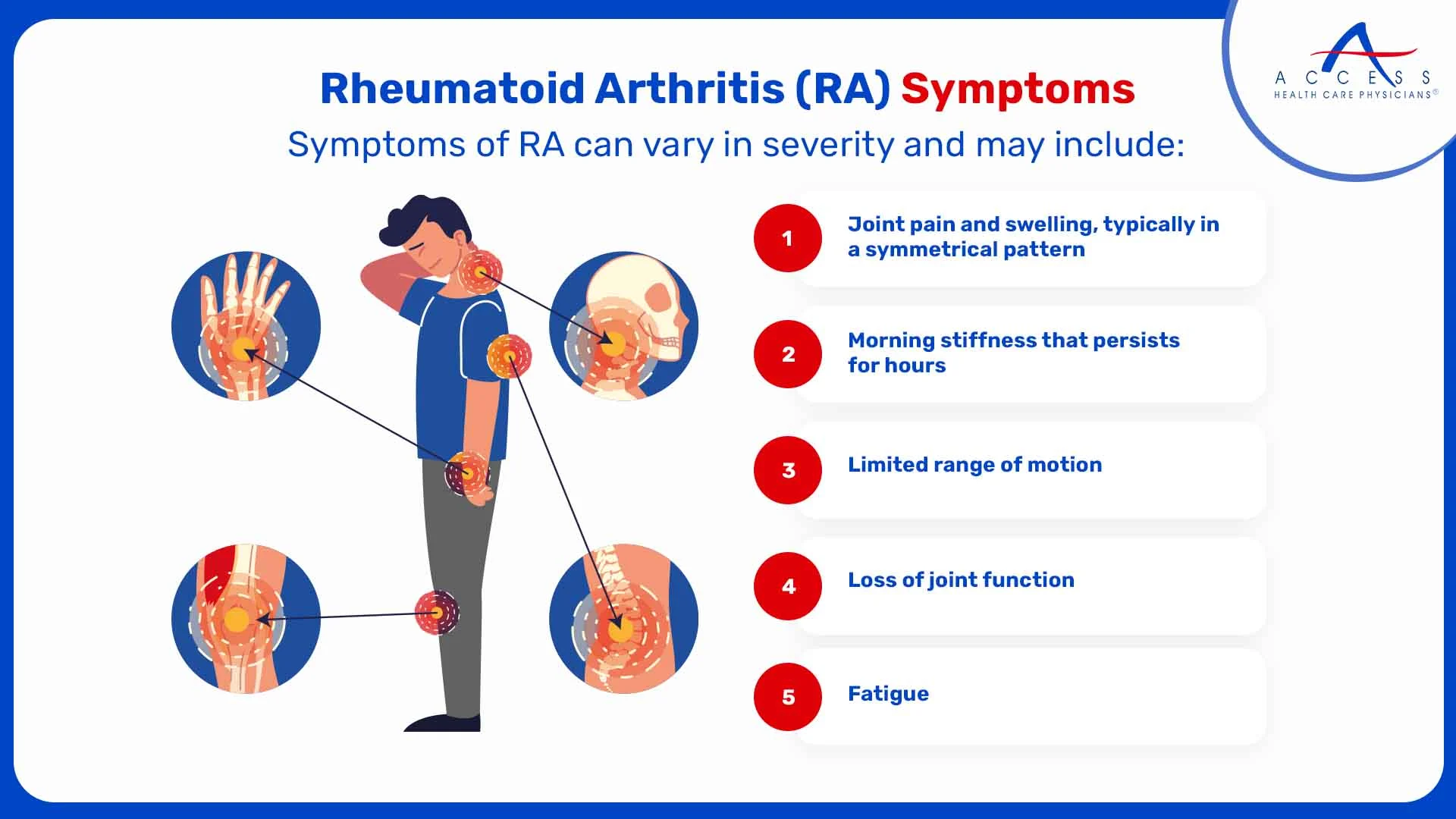
- Joint pain and swelling, typically in a symmetrical pattern
- Morning stiffness that persists for hours
- Fatigue
- Loss of joint function
- Limited range of motion
RA often requires long-term management with medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis can help slow the progression of the disease and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, often known as Lupus, is a complicated autoimmune illness that can impact different body systems and organs.
Numerous symptoms can appear with lupus, making diagnosis and treatment challenging. Women are more likely to experience it, especially when they are childbearing.
Common symptoms of lupus may include:
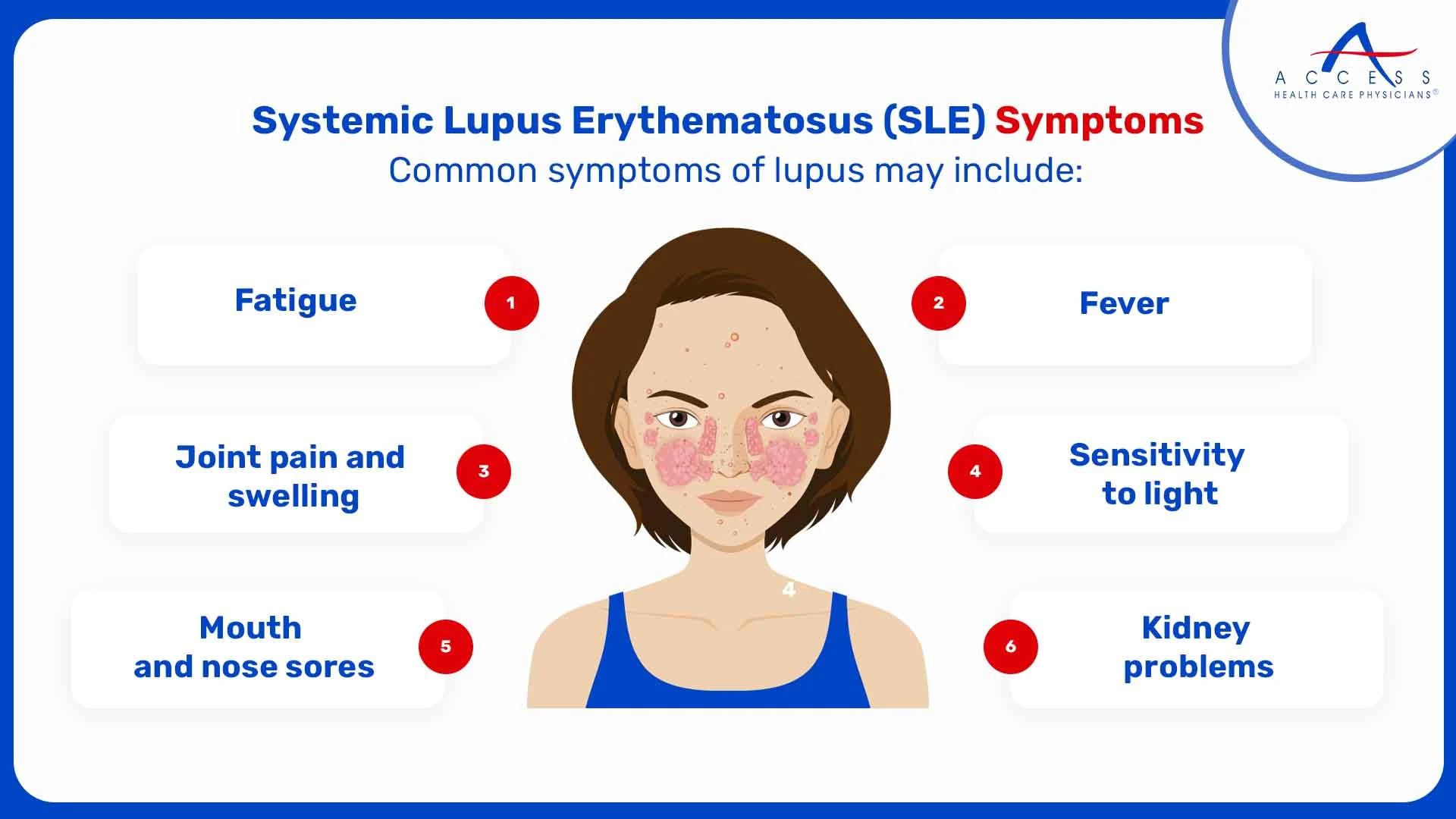
- Fatigue
- Joint pain and swelling
- Skin rashes, often triggered or worsened by sun exposure
- Kidney problems
- Fever
- Sensitivity to light
- Mouth and nose sores
Lupus is known for its unpredictable flares and remissions. Treatment often involves medications to control symptoms and suppress the immune system's abnormal response.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (juvenile diabetes) is an autoimmune illness that affects the pancreas. The immune system targets and kills the pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin in people with type 1 diabetes.
As a result, there is insufficient insulin, a hormone that is vital for controlling blood sugar levels.
Insulin pumps or routine insulin injections are necessary for the management of type 1 diabetes. To maintain optimum health, patients need to closely monitor their food, physical activity, and blood sugar levels.
High blood sugar levels can cause serious side effects, such as renal disease, nerve damage, and heart diseases if left untreated.
Common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
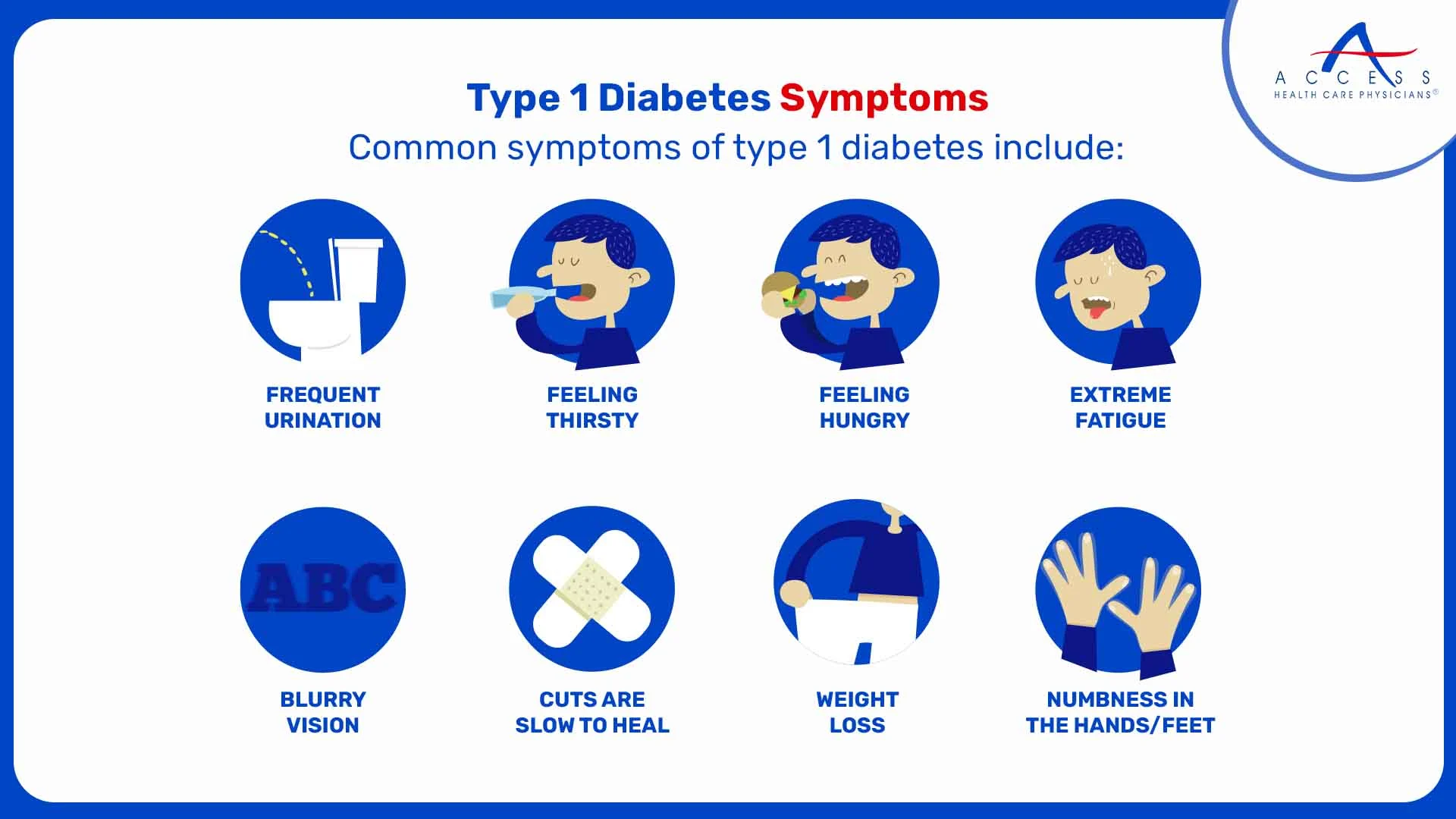
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
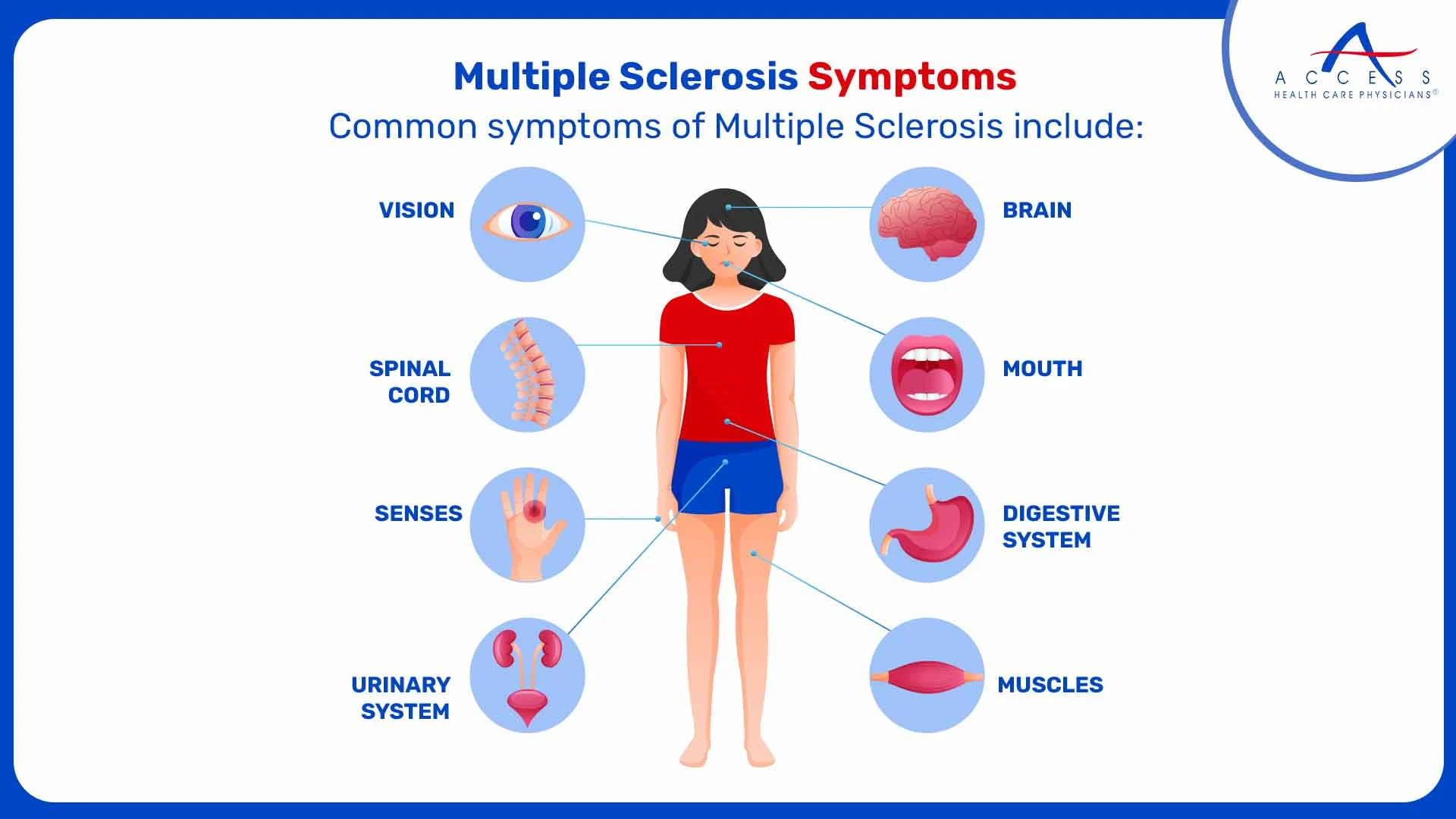
Multiple Sclerosis
An autoimmune neurological condition called multiple sclerosis affects the brain and spinal cord as well as the central nervous system.
The immune system attacks the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibers in multiple sclerosis (MS), causing inflammation and nerve damage.
MS symptoms can vary widely among individuals and may come and go.
Treatment typically involves disease-modifying medications to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses, along with therapies to manage specific symptoms.
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland, a small, butterfly-shaped organ in the neck that regulates metabolism.
In Hashimoto's, the immune system targets and damages the thyroid tissue, leading to an underactive thyroid, a condition known as hypothyroidism.
Common symptoms of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis include:
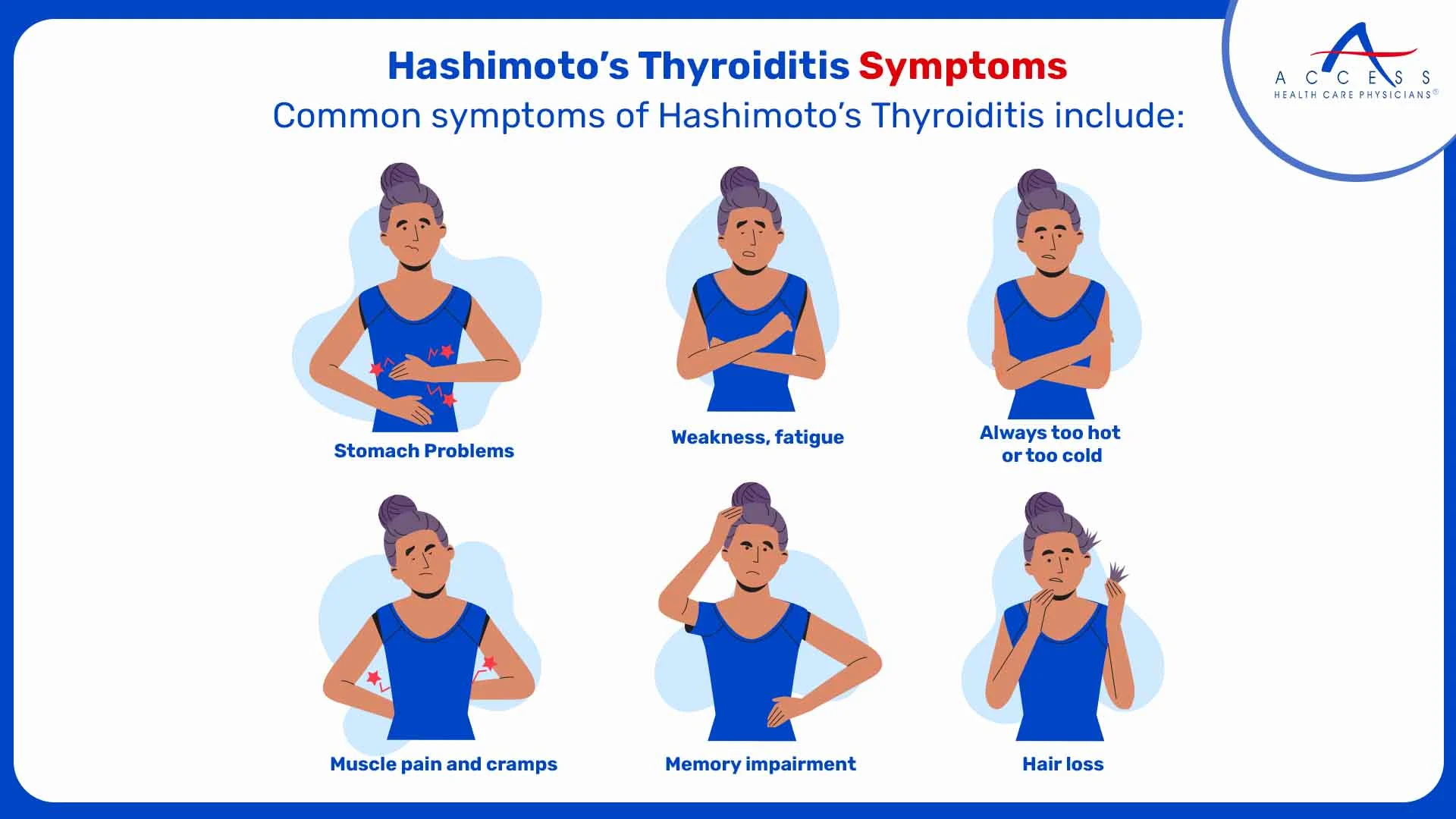
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Muscle and joint pain
- Dry skin
- Depression
- Constipation
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is triggered by the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat. When someone with celiac disease ingests gluten, their immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine, leading to inflammation and damage. This can interfere with the absorption of nutrients from food and cause a wide range of digestive systemic symptoms.
Common symptoms of celiac disease include
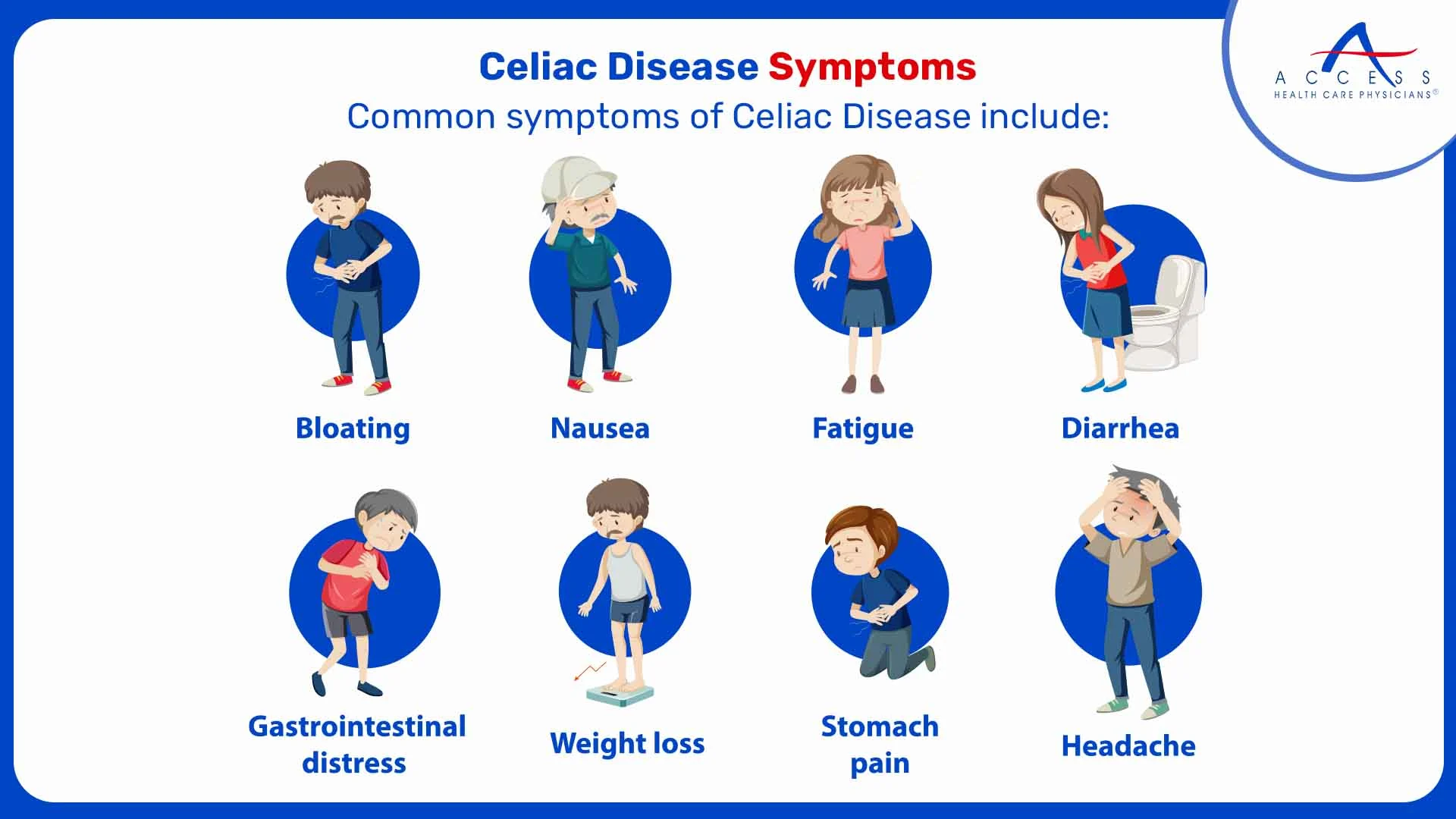
- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Skin rashes (dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Headaches
- Joint pain The main treatment for celiac disease is a gluten-free diet. Adhering to this diet can lead to symptom relief and the healing of intestinal damage.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis primarily affects the skin but can also have systemic effects on the body. It results from an overactive immune response that triggers the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to the development of raised, red, and scaly patches.
Common types of psoriasis include:
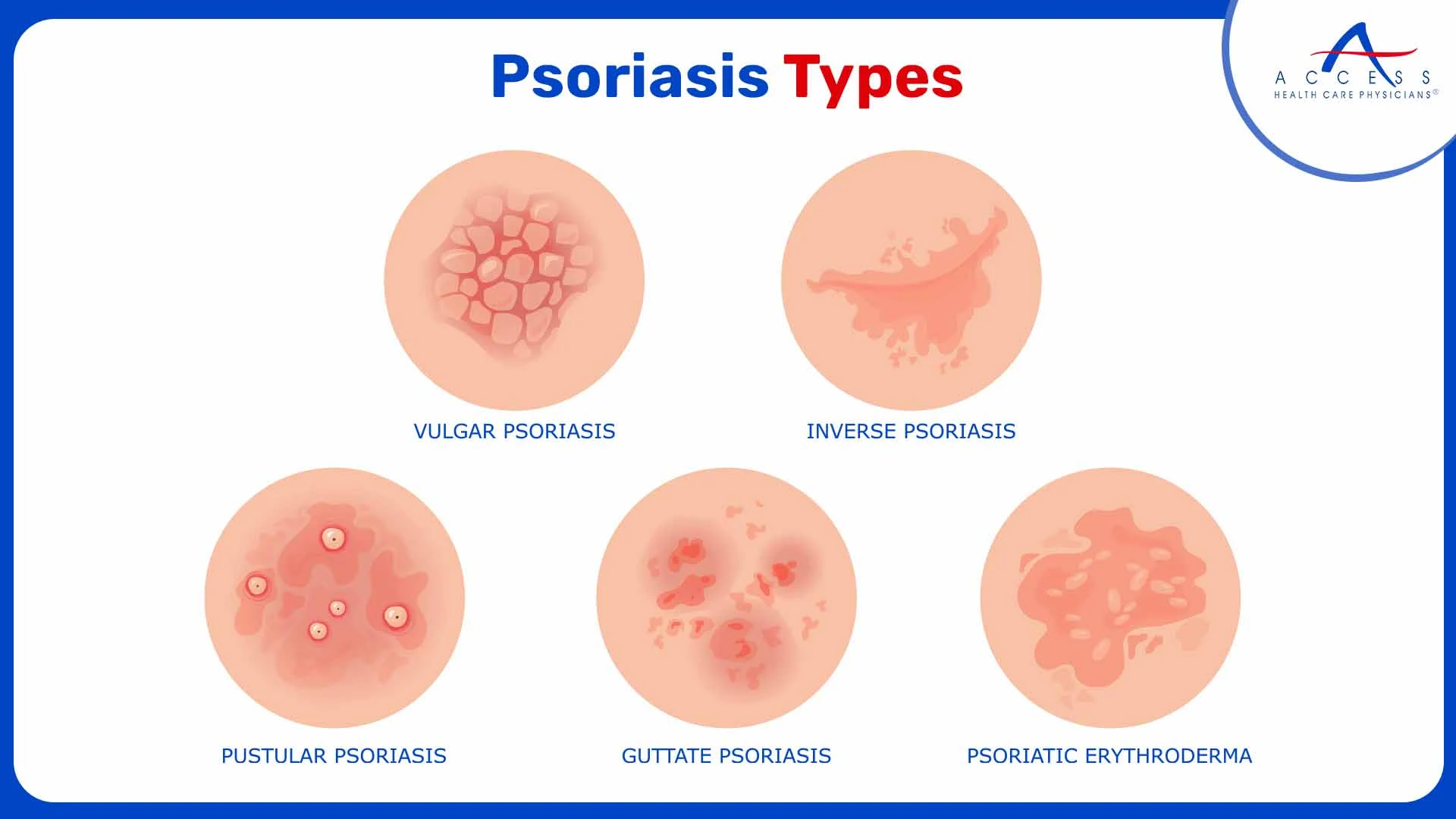
- Plaque psoriasis
- Guttate psoriasis
- Inverse psoriasis
- Pustular psoriasis
- Erythrodermic psoriasis
Psoriasis can be associated with other autoimmune conditions, such as psoriatic arthritis.
Treatment options include topical creams, light therapy, oral medications, and biological drugs, depending on the severity of the condition.
Autoimmune diseases can have significant adverse effects on the quality of life of people impacted and frequently call for long-term care. If you or someone you know is experiencing for symptoms suggestive of an autoimmune disease, it's essential to seek medical evaluation and diagnosis promptly. Contact Access Health Care Physicians for early detection and appropriate treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lupus, Rheumatoid arthritis, and Type 1 diabetes are the most autoimmune diseases.
Rheumatoid arthritis can be a very complex autoimmune disease to deal with.
While there is generally no complete cure for autoimmune illnesses, they can often be managed with the right medical care.


