Do you often wake up feeling tired and worn out, even after a full night’s sleep? Everyone has felt the effects of sleep deprivation at some point, leaving many to wonder about its lasting impacts and potential solutions.
For some people, sleep loss is sometimes worn as a badge of honor— a sign they are getting things done. In our fast-paced modern world, sleep is often sacrificed in the pursuit of productivity and success. But chronic sleep deprivation is a serious concern that can have significant implications for your overall health, particularly your brain health.
Sleep deprivation can negatively affect your mood and cause cognitive impairment.
The Science of Sleep
It's important to comprehend the fundamentals of sleep before diving into the consequences of sleep deprivation on the brain. Each stage of the complex physiological process that is sleep is essential for its restorative effects.
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-REM sleep are the two primary categories of sleep. Vivid dreams are connected to REM sleep, which is also thought to enhance memory consolidation and emotional processing. On the other hand, non-REM sleep is broken down into three stages, the third of which is the deepest and most restorative.
The brain performs necessary functions like memory consolidation, toxin elimination, and neuronal repair while we sleep. To keep the brain healthy and cognitive function at its highest level, these processes are extremely essential. This delicate equilibrium can be disrupted by sleep deprivation, which can have a significant impact on many aspects of brain activity.
Symptoms of sleep deprivation
The cognitive effects of sleep deprivation are obvious - you are more forgetful, less capable to concentrate, and more likely to have accidents. Poor sleep also has a negative impact on your ability to manage stress and maintain mental wellness.
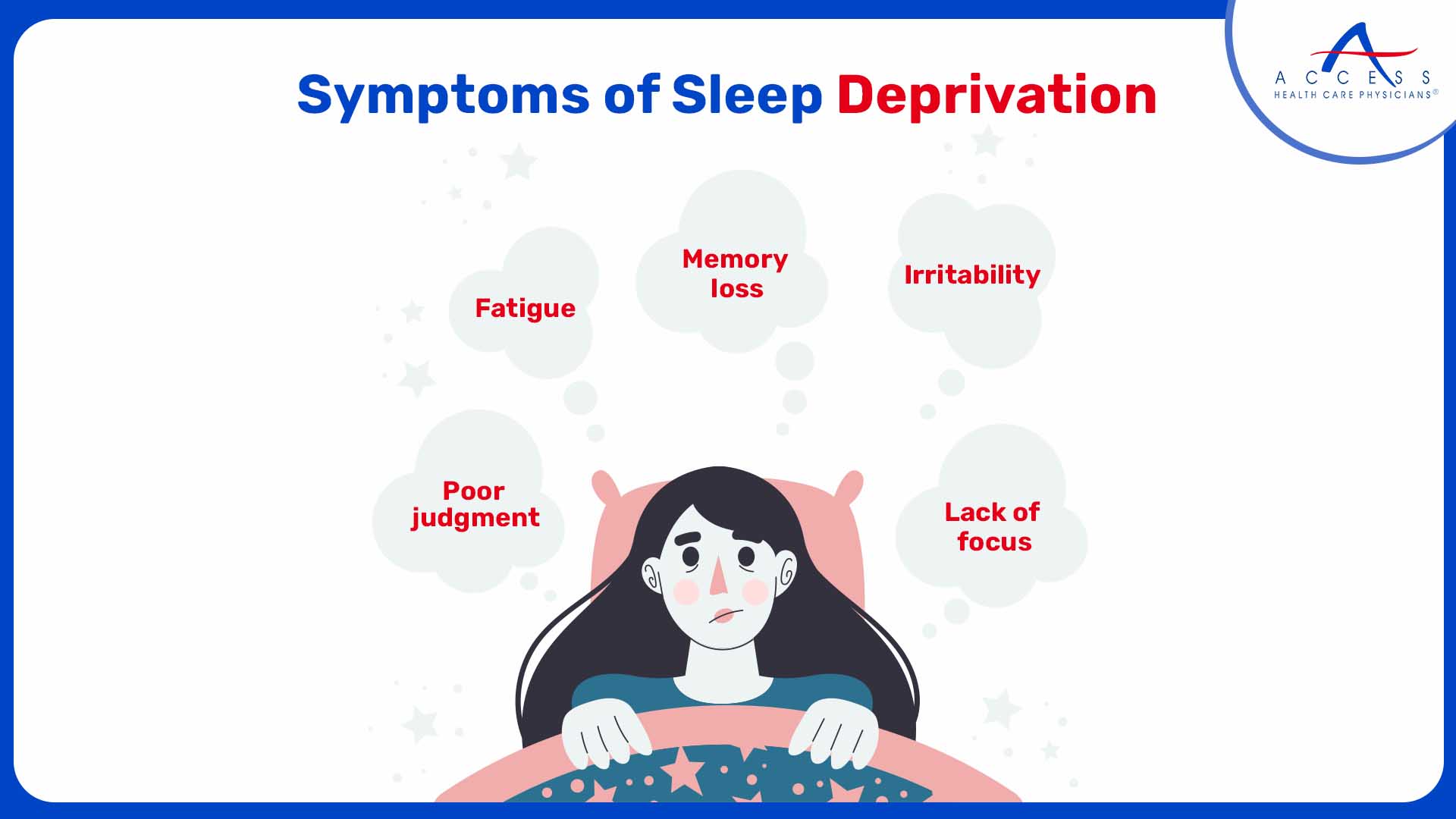
Here are some commonly experienced symptoms -
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Memory loss
- Lack of focus and motivation
- Poor judgment
Effects on Cognitive Function
One of the most noticeable impacts of sleep deprivation is its effect on cognitive function. Sleep is closely linked to learning and memory. Adequate sleep supports the brain's ability to consolidate information gathered during the day, facilitating the formation of long-term memories. Chronic sleep deprivation, however, impairs this process, leading to difficulties in retaining and retrieving information.
Lack of sleep seriously impairs one's ability to pay attention, concentrate, and solve problems. Studies have shown that even one night of insufficient sleep can cause a drop in alertness and impair the capacity to concentrate.
It is vital to prioritize regular, peaceful sleep to preserve normal brain function because prolonged sleep deprivation can resemble the cognitive impairments seen in people with certain neurological illnesses.
Emotional Regulation and Mood
Sleep and emotional health are closely related. Lack of sleep can heighten unpleasant emotions including irritation, anxiety, and melancholy. In reaction to lack of sleep, the amygdala in the brain, which processes emotions, becomes hyperactive, while the prefrontal cortex, which controls emotional responses, finds it difficult to exercise its inhibitory control. This imbalance may lead to changes in mood and a reduced capacity for stress management.
Lack of sleep increases the chance of developing mood disorders such as anxiety and depression. People who have these conditions frequently have disturbed sleep patterns, which leads to a vicious cycle in which sleep issues worsen emotional disturbances and vice versa. Making getting enough sleep a priority might be crucial for fostering emotional fortitude and preserving healthy mental health.
Impact on Creativity and Innovation
Innovation and creativity are fueled by the brain's ability to form novel connections between ideas and concepts. Sleep has been shown to enhance this creative process through the consolidation of information and the reorganization of neural networks. During REM sleep, the brain engages in a unique form of information processing that encourages the integration of seemingly unrelated information, contributing to "aha moments" and breakthroughs.
Physical Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
The impact of sleep deprivation extends beyond cognitive and emotional realms to physical health. Sleep plays a critical role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, immune response, and hormone production. Chronic sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even certain cancers.
Sleep Deprivation and Brain Health
From a brain health perspective, sleep deprivation has been linked to a higher likelihood of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. During sleep, the glymphatic system, a waste clearance system in the brain, becomes more active, facilitating the removal of toxic waste products that accumulate during wakefulness. Sleep deprivation impedes this process, potentially contributing to the buildup of harmful protein aggregates that characterize neurodegenerative diseases.
Tips for Promoting Restful Sleep
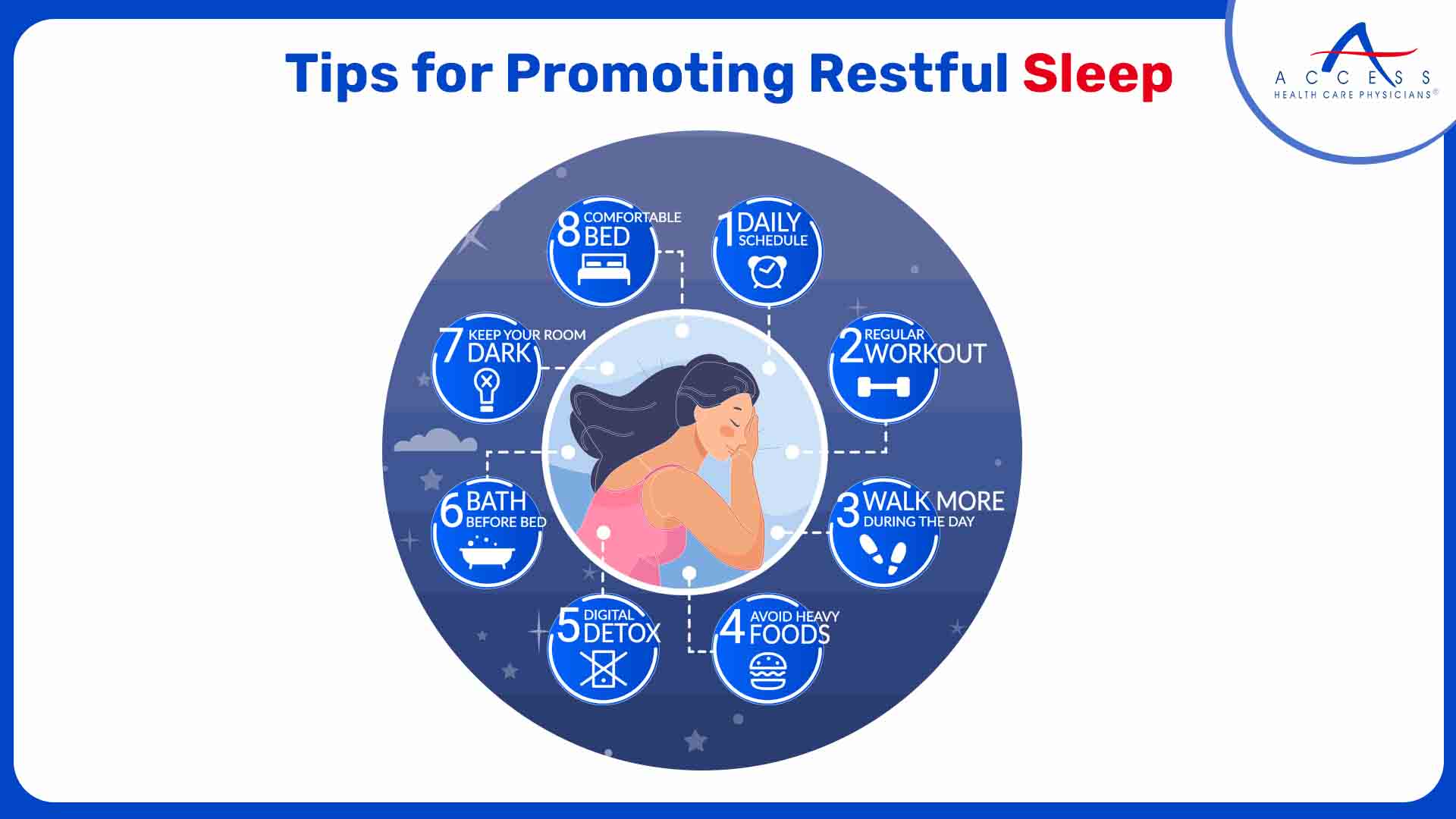
In recognizing the impact of sleep on brain health, it's essential to prioritize healthy sleep habits. Here are some tips and tricks to promote healthy sleep.
- Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment
- Practice Regular Physical Activity
- Mind Your Diet
- Manage Stress.
- Limit Screen Time
- Seek Professional Help
Lack of sleep is a quiet epidemic that adversely affects mental and physical health. Making sound sleep a priority is an essential step to preserving excellent brain health and ensuring that you can function at your peak both cognitively and physically. Reach out to a healthcare professional via Access Health Care Physicians to learn more about sleep health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lack of sleep not only impairs judgment and rational cognition but also weakens memory.
The available data and ongoing studies suggest that brain damage caused by sleep deprivation is reversible.
A good 7-8 hours of uninterrupted sleep is recommended by experts.


