Few disorders in the field of healthcare demand as much dedication and devotion as hyperglycemia. For those with diabetes, hyperglycemia—which is defined as elevated blood sugar—is a common cause for concern.
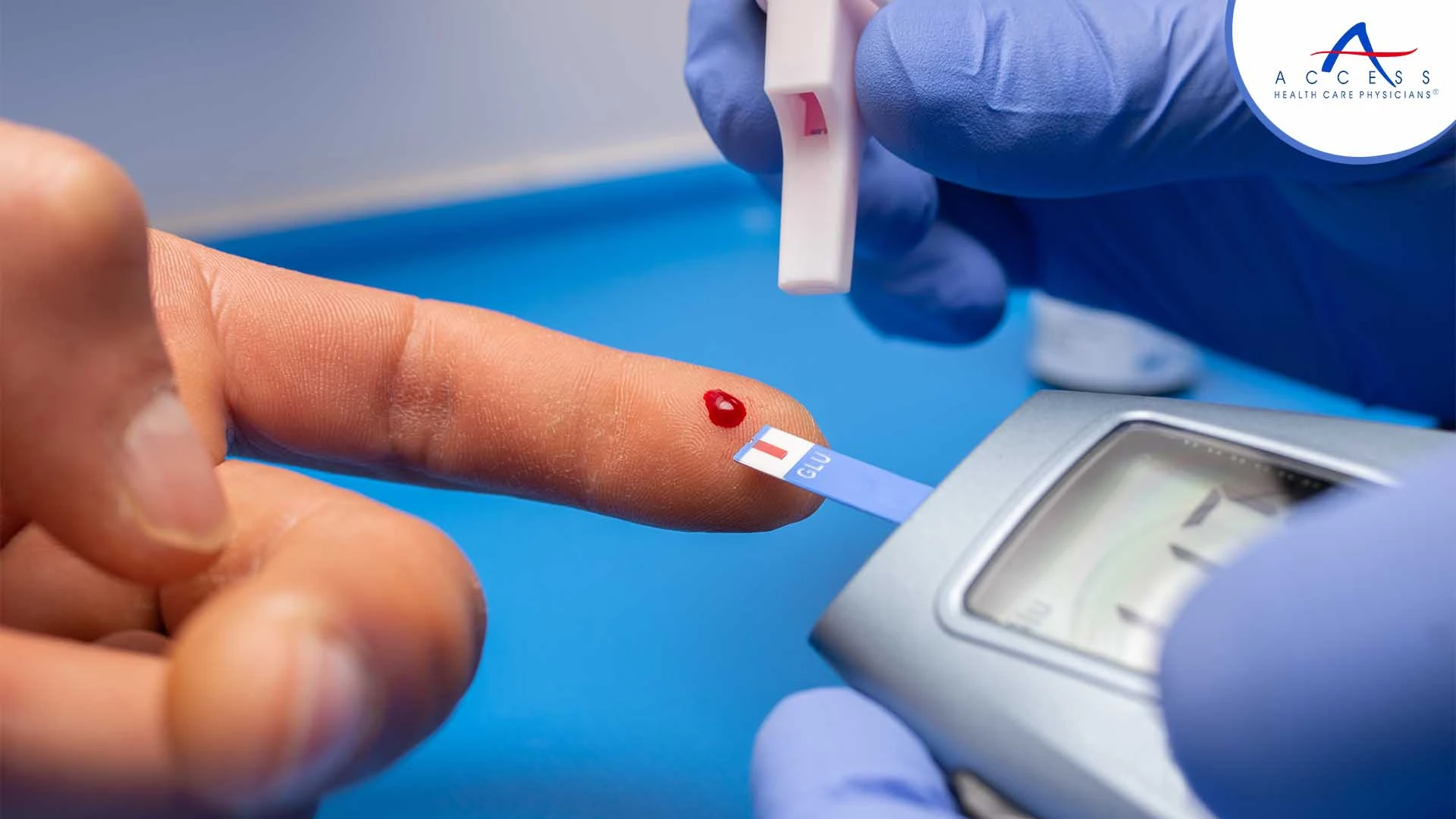
It is hard to overestimate the significance of routine blood sugar monitoring because it is an essential tool for properly managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia is characterized by high blood glucose (sugar) levels and it mostly affects those with diabetes, a chronic illness in which the body has difficulty controlling blood sugar levels. Diabetes comes in two primary forms: Type 1 and Type 2.
The immune system of the body unintentionally targets and kills the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, resulting in type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune disease. Since it makes it easier for glucose to enter cells, the hormone insulin is essential for controlling blood sugar levels. Hyperglycemia results from elevated blood sugar levels caused by insufficient insulin.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin. The pancreas initially makes up for this by manufacturing more insulin, but eventually, it might not be able to meet the body's needs.
What Causes Hyperglycemia?
In addition to diabetes, several other conditions can cause hyperglycemia as well. These include hormonal fluctuations, sickness, stress, certain prescription medications, and insufficient physical activity.
Managing and avoiding hyperglycemia requires a holistic approach, involving an understanding of these underlying components.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
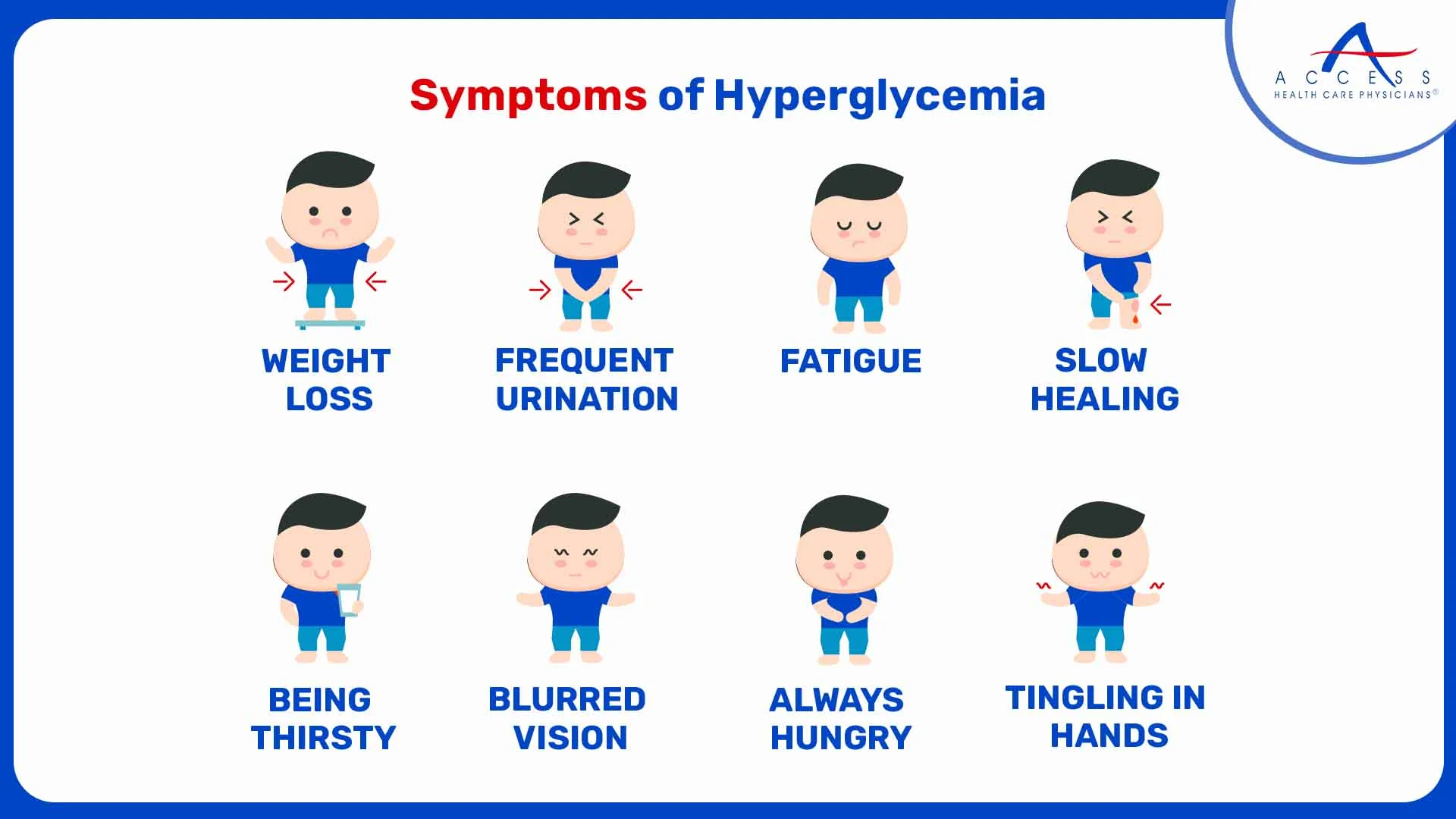
- Increased Thirst and Urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred Vision
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Slow Healing of Wounds
- Recurrent Infections
Complications of Hyperglycemia
If left unmanaged, hyperglycemia can result in severe complications, impacting various organs and systems within the body.
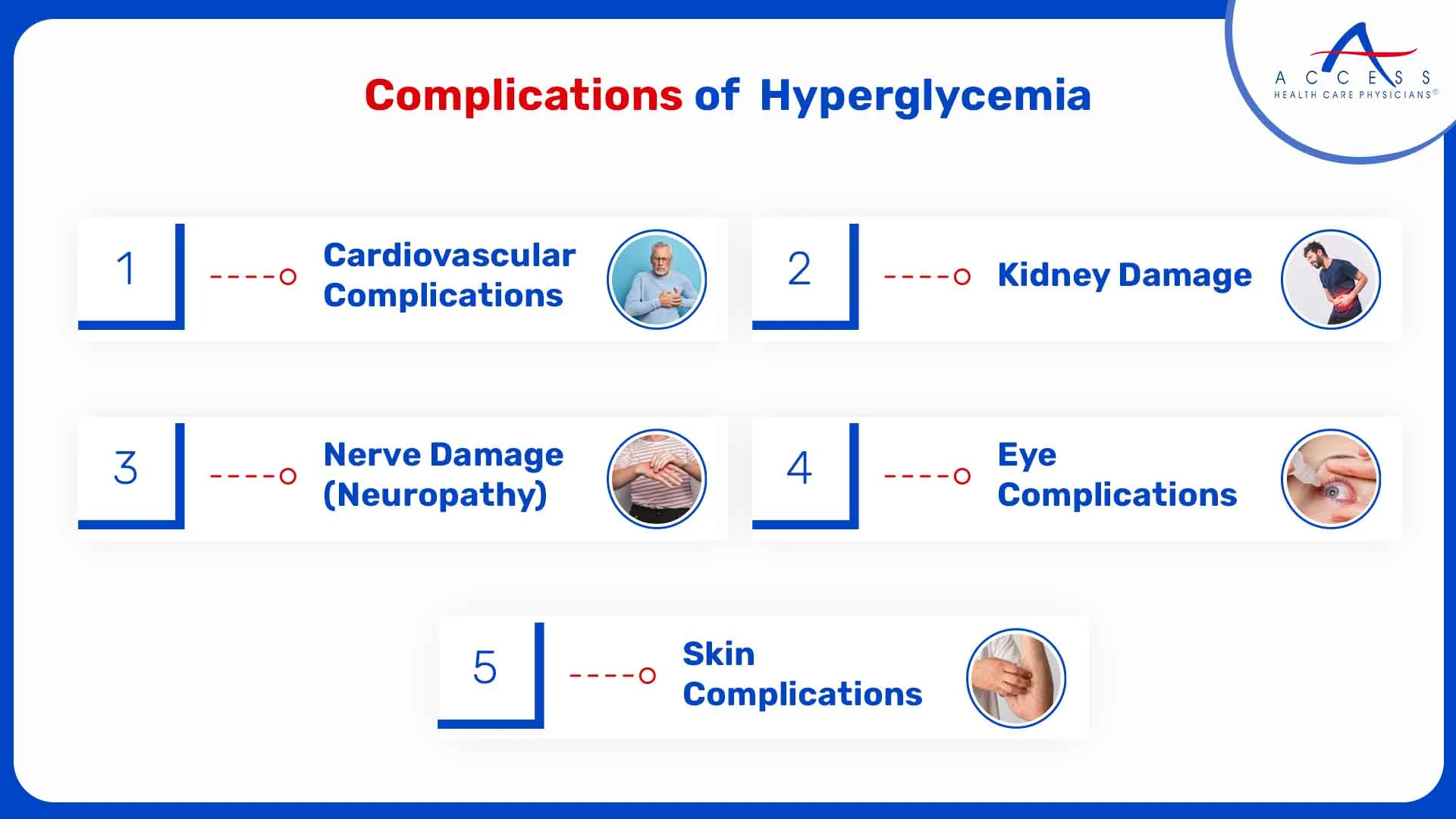
Some of the potential complications include:
- Cardiovascular Complications
One of the main risk factors for cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes is hyperglycemia. High blood sugar levels play a significant role in the onset of atherosclerosis, a disorder that causes arteries to stiffen and narrow.
- Kidney Damage
Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can lead to kidney damage, eventually progressing to chronic kidney disease (CKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Prolonged hyperglycemia can harm nerves, resulting in symptoms including tingling, numbness, and discomfort in the limbs. Diabetic neuropathy is a disorder that can seriously lower quality of life.
- Eye Complications
Elevated blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to diabetic retinopathy and, in severe cases, vision loss.
- Skin Complications
Skin conditions such as bacterial and fungal infections are more common in individuals with hyperglycemia due to impaired immune function and slower wound healing.
Why Should I Monitor My Blood Sugar?
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for the efficient management of diabetes in individuals. Keeping an eye on blood sugar levels gives important information about how the body is reacting to medication and lifestyle changes.
It supports people in making informed choices about dietary modifications, medication adjustments, and overall diabetes management techniques with their healthcare providers.
Situations That Typically Cause A Blood Sugar Rise
- Consuming excess carbohydrates
- Missing your diabetes dose
- High levels of stress
- Dehydration
- Taking sterioid medicines
Ways to Monitor Blood Sugar
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG)
SMBG involves using a blood glucose meter to measure blood sugar levels at home. This method provides instant results and allows individuals to make immediate adjustments to their treatment plan based on the readings.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM involves wearing a small sensor under the skin that continuously measures glucose levels throughout the day and night. This real-time data helps individuals and healthcare providers identify patterns and trends, leading to more personalized and effective management strategies.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test
The hemoglobin A1c test provides a snapshot of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. This test is typically performed in a healthcare setting and offers a broader perspective on overall diabetes management.
How Often Should I Monitor My Blood Sugar?
The type of diabetes, the course of therapy, and an individual's general health may all affect how frequently blood sugar is checked. It is generally recommended that people with diabetes check their blood sugar several times a day, particularly before meals, after meals, and right before bed.
Implementing Lifestyle Modifications
- A well-balanced diet is pivotal in managing blood sugar levels and preventing hyperglycemia. This includes monitoring your carbohydrate intake and working with dietitians to create a personalized carbohydrate counting plan.
- Controlling portion sizes is important for preventing overconsumption of calories and carbohydrates. Eating smaller, balanced meals throughout the day can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Regular physical activity benefits individuals with diabetes, as it helps improve insulin sensitivity and promotes overall health. Exercise can include aerobic activities, strength training, and even walking.
- Adhering to prescribed medications, including insulin, is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Overcoming Barriers to Blood Sugar Monitoring
- Access to blood glucose monitoring tools and supplies can be a significant barrier for some individuals. Healthcare providers and organizations should work to address these financial barriers by exploring affordable monitoring options and connecting individuals with assistance programs.
- Emotional and psychological factors can impact an individual's commitment to blood sugar monitoring. Fear, anxiety, and burnout are common challenges.
- As technology continues to play a crucial role in diabetes management, some individuals may face technological barriers, such as difficulty using glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring devices.
When Should I Call My Doctor?
Consult with your provider if you frequently experience symptoms or blood sugar swings, regardless of whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. They can recommend modifying your diabetes treatment plan accordingly.
In conclusion, understanding hyperglycemia and the importance of regular blood sugar monitoring is paramount for individuals with diabetes. Hyperglycemia, if left uncontrolled, can lead to severe complications affecting various aspects of health.
Reach out to a primary care doctor at Access Health Care Physicians for further consultation and treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
The most important thing you can do to treat type 1 or type 2 diabetes is to regularly check your blood sugar. This will help you observe the factors that influence your results, such as dietary changes, medication compliance, and physical activity.
Steady insulin levels throughout the day are extremely important to regulate blood sugar levels.
Common symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst, blurred vision, and unintentional weight loss.