Not surprisingly, anxiety disorders have become a more common problem in a world where life seems to be moving at an ever-increasing pace. There are many different types of anxiety disorders that impact people from all walks of life, ranging from minor concerns that interfere with our everyday activities to the crippling panic that may consume our lives.
Anybody can get anxious. An anxiety disorder, however, could potentially be the reason why overpowering levels of worry and distress keep us from going about our daily lives. Depression and anxiety are often closely linked.
What Are Anxiety Disorders?
Excessive concern, fear, or apprehension are hallmarks of a mental health illness known as anxiety disorder. Everyone experiences anxiety at some point in their lives, but when it starts to interfere with day-to-day activities and quality of life, anxiety becomes a disorder. It's usually difficult to get through the day when anxiety takes over.
Types and Subtypes of Anxiety Disorder
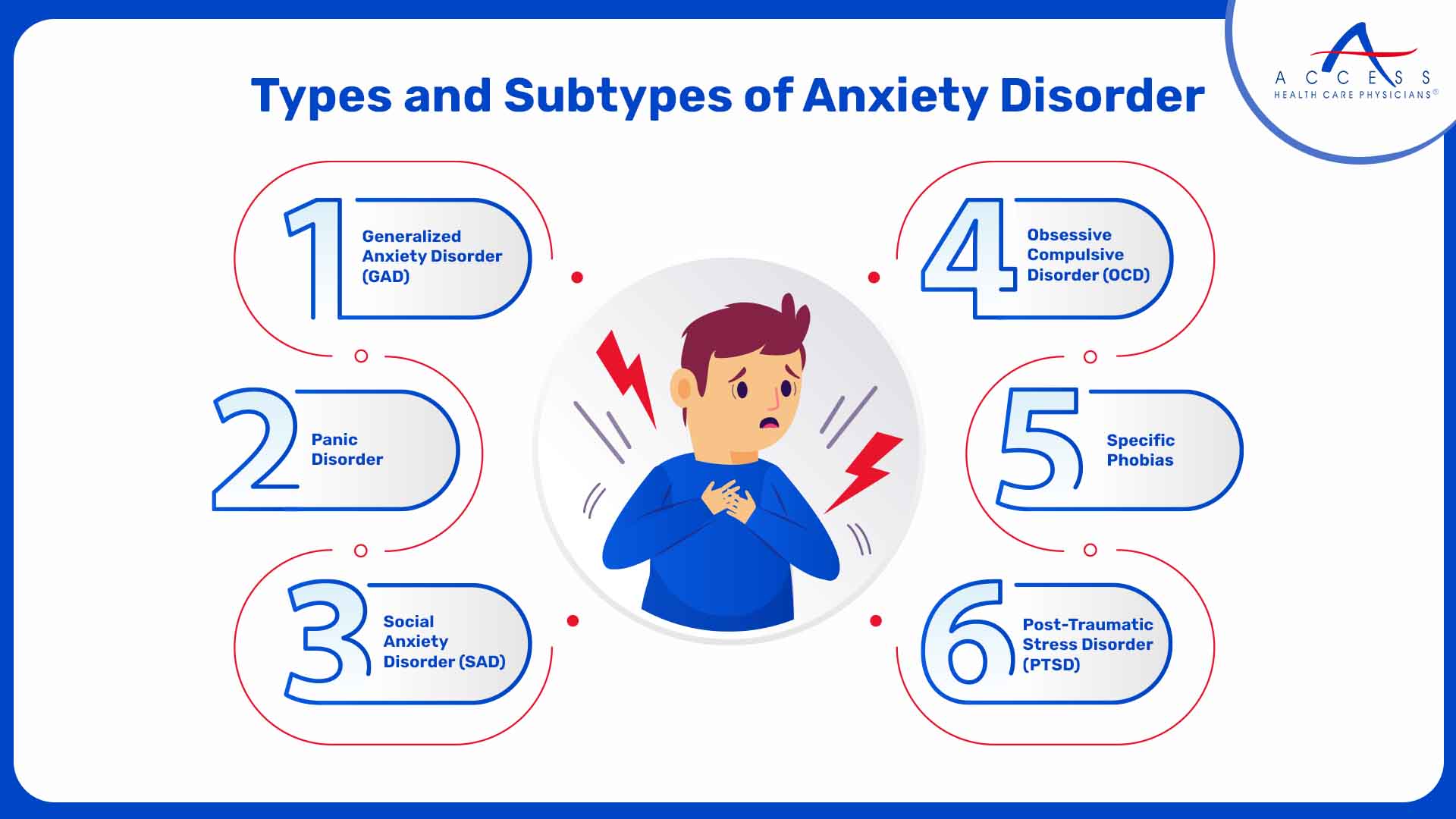
There are several main types of anxiety disorders, each with its own unique characteristics:
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
Extreme, ongoing concern over a variety of life events is a common symptom of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), frequently without a clear reason or trigger. Physical symptoms such as weariness, muscle tension, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating could stem from this ongoing mental condition.
2. Panic Disorder:
Panic disorder is characterized by recurrent and unplanned panic attacks, which are brief bursts of intense fear accompanied by bodily symptoms such as sweating, shaking, a racing heart, and a sense of impending doom. Living a constrained lifestyle and engaging in avoidance behaviors can result from the dread of suffering another attack.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD):
A different term for this condition is social phobia disorder (SAD). It is characterized by intense anxiety about being scrutinized by others and social situations. SAD sufferers frequently steer clear of social events, speaking engagements, and other circumstances in which they can draw attention to themselves.
4. Specific Phobias:
These include unreasonable and extreme phobias of particular things or circumstances, such as flying, heights, spiders, or needles. The phobic stimuli can cause excruciating anxiety and terror.
5. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
Even though OCD is frequently categorized as an anxiety disorder, it is distinguished by intrusive thoughts, obsessions, recurrent actions, or compulsions, carried out to reduce the distress associated with those obsessions.
6. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
People who have post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are prone to experiencing flashbacks, nightmares, and intense anxiety when reminded of a catastrophic event. It can seriously hinder their ability to function on a daily basis.
Causes and Triggers
There is not one reason for anxiety disorders; rather, a variety of factors. These include personality, events in life, brain chemistry, and heredity, which tend to contribute to the medical condition.
Having a thorough understanding of these variables can help identify the underlying causes of anxiety disorders and develop efficient treatment strategies.
1. Genetics and Family History:
If you have a family member with a history of anxiety disorder, you might be at a higher risk of developing one too. Certain genes tend to play a significant role in how your brain responds to stress and fear.
2. Brain Chemistry:
Serotonin, dopamine, and GABA are examples of neurotransmitters that are important for mood and anxiety regulation. Anxiety disorders may arise as a result of an imbalance in these neurotransmitters.
3. Environmental Factors:
The unexpected loss of a loved one, abuse, or other traumatic life events can set off anxiety disorders, particularly post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). An increased risk factor may also include a history of previous mental health issues and chronic stress.
4. Personality Traits:
Anxiety disorders are more common in people who tend to have poor self-esteem, a perfectionist mindset, or a history of excessive anxiety. These characteristics can worsen the effects of stress in life.
5. Brain Structure:
Studies have shown that certain brain structures, such as the amygdala (involved in processing emotions) and the prefrontal cortex (involved in decision-making), may be different in people with anxiety disorders.
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
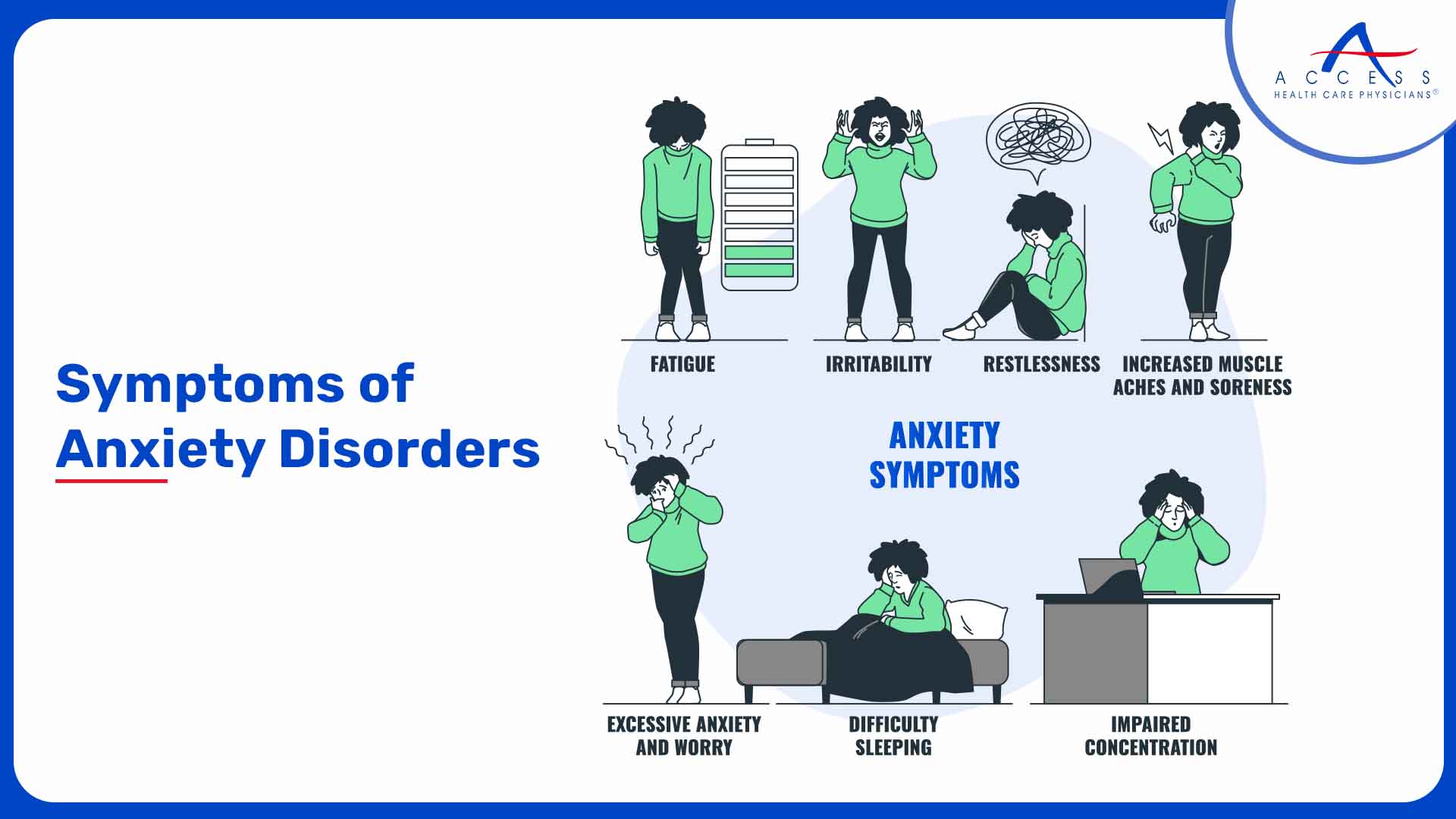
Recognizing the signs of anxiety disorders is essential for seeking timely professional help and support. While specific symptoms can vary depending on the type of anxiety disorder, some common symptoms include:
- Excessive Worry
- Physical Symptoms such as restlessness, fatigue, muscle tension, sweating, and heart palpitations
- Avoidance Behavior
- Panic Attacks
- Frequent Negative Thinking
- Trouble falling asleep
- Irrational Fears
Treatment and Management
Although recovering from an anxiety disorder can be difficult, it's important to understand that there are useful techniques and therapies out there.
For those with anxiety disorders, a mix of therapy, lifestyle modifications, and, in certain situations, medication can greatly enhance the quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a popular therapy that seeks to recognize and modify harmful thought patterns and behaviors that fuel anxiety.
Exposure Therapy: Particularly effective for phobias and OCD, exposure therapy involves gradually and safely confronting anxiety-triggering situations to reduce fear and anxiety over time.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation can help manage anxiety by promoting relaxation and self-awareness.
Lifestyle Adjustments:

- Physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters that can help reduce anxiety.
- A balanced diet rich in whole foods and nutrients can positively impact both physical and mental health.
- Prioritize sleep hygiene to ensure restful sleep, as sleep deprivation can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol. Both substances can exacerbate anxiety and disrupt sleep patterns.
Breaking the Stigma: Speaking Up About Anxiety
A significant barrier to getting treatment for anxiety disorders is the stigma attached to mental health. It is imperative to cultivate a culture that values and accepts candid discussions regarding mental health. Access Health Care Physicians helps in removing these impediments and building a community that is more tolerant and compassionate.
Anxiety disorders might feel overwhelming, but with the right support and treatment, they can be managed effectively. Connecting with a mental health professional, such as a psychologist, or even a primary care doctor can provide guidance and customized treatment plans. Additionally, building and nurturing relationships with friends and family members can provide a strong emotional foundation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Examples of relaxation methods that help reduce anxiety include yoga, meditation, and visualization exercises.
Anxiety disorders cannot be cured by medication. However, they can reduce symptoms and enhance your ability to perform.
Anxiety disorders can make it difficult for a person to work, study, and do daily tasks. They can also cause social isolation and clinical depression. Additionally, it could damage ties with family, friends, and coworkers.
Stressful events that take place during childhood, adolescence, or adulthood are frequently the cause of anxiety disorders. Being exposed to stress and trauma when you're very young is likely to have a significant effect.


