Osteoporosis is the most common bone disease, affecting more than 44 million US adults. Osteoporosis is a disease that occurs when the body’s bone density is very low. In fact, the name osteoporosis actually means ‘porous bone.’
To truly understand what osteoporosis is, we must first have an understanding of bone structure. It may be easy to think of bone as lifeless, rigid and hard. However, this is not the case. Your bones are living and growing tissue. Healthy bone actually looks more like honeycomb when viewed through a microscope. With osteoporosis, these gaps in the bone become larger which weakens the bone and increases the risk of fractures. These fractures are most common in the hip, spinal vertebrae and joints such as the wrist.
What are the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Often, osteoporosis develops so slowly there are no symptoms of the disease before a break or fracture. In fact, it has even been referred to as a “silent disease” for this reason.
You should see a doctor if you experience height loss, severe back pain, pain that may indicate a fracture or break, curved spine or stooped posture.
How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
Your doctor will begin by discussing your family medical history and any risk factors. If they suspect bone density loss, they may request a bone mineral density scan (BMD.) This type of scan using a type of X-ray called dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, which you may have heard referred to as a DEXA scan. These tests are quick and painless.
There are two types of DEXA scans:
- Peripheral Device – this is a mobile machine that tests bone in the wrist, heel or finger.
- Central Device – this scan is typically a hospital or imaging center-based scan, which the patient will lay on a bed while the scan measures hip and spine bone mineral density.
The results of the DEXA scan will be given as a “T Score.” This score compares the patient’s bone mass to that of a younger, healthier person.
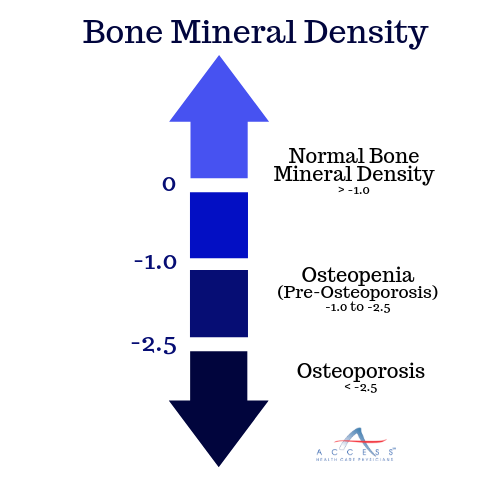
What are the treatments for osteoporosis?
In the event you doctor diagnoses you with osteoporosis or osteopenia (pre-osteoporosis) they may recommend a few treatment options. These treatments are intended to slow down or stop bone loss and help rebuild or strengthen bones. The treatments for osteoporosis are intended to help prevent fractures, reduce pain and maximize the quality of life.
There are several medications that can be used to help treat osteoporosis and help prevent further bone loss which may include hormonal therapy or immune therapies. In addition to medications, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes such as your diet or exercise routines. A few of these ideas are mentioned below.
What are the risk factors for osteoporosis?
There are several risk factors associated with an increased risk of developing osteoporosis, which may include the following:
- Age – Bone begins to weaken beginning at the age of 35. According to the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF,) once a person reaches 50 years in age, 1 in 3 women and 1 in 5 men will experience osteoporosis-related fractures.
- Hormone Loss – Low levels of estrogen have been linked to bone loss.
- Caucasian or Asian ethnicity have a higher risk of developing osteoporosis than other ethnic groups.
- Body Weight and Height – Being over 5’ 7” tall or having a small bone structure or weight increases the risk of developing osteoporosis.
- Family history of osteoporosis.
- Lifestyles that include inactivity or diets low in calcium or vitamin D.
- Certain medications have also been shown to weaken bones.
- Smoking or drinking alcohol
What can I do to reduce my risk of developing the risk of osteoporosis?
There are many steps you can take to help keep your bones healthy.
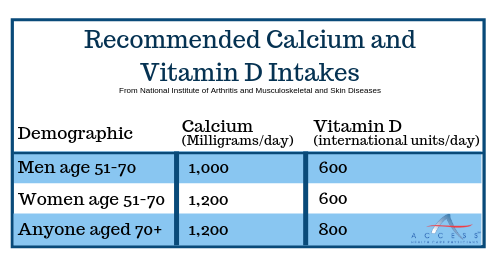
1. Enjoy a healthy diet rich in calcium – Calcium helps to build bones and also helps to keep them strong, helping to prevent fractures. Try foods including dark green leafy vegetables such as collards and kale, canned fish like salmon and low-fat dairy products.
2. Ensure you are getting plenty of vitamin D – Vitamin D is essential for your body to absorb the calcium you are eating. This is why often, you will see dairy products with vitamin D added, which is known as “fortified.” You can also get vitamin D from the sun, fatty fish, eggs and other fortified foods and drinks.
3. Avoid lifestyle choices such as smoking and drinking alcohol, which may increase your risk of osteoporosis and many other diseases.
4. Be sure to remain physically active, as advised by your physician. There are many types of physical activities that help to strengthen bones including; Tai Chi, weight-bearing exercise (like walking) and strength training.
Another important factor in preventing fractures is fall prevention. Falls are the number one cause of injury to older adults in the US. Regular exercise, along with a few safety checks in the home can help to prevent falls. To learn more about fall prevention, click the image below:

Unfortunately, osteoporosis is common and can cause the overall quality of life to suffer. However, by being proactive, you can help to reduce your risk of developing osteoporosis or slow down the progression of bone loss. Enjoy a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, get plenty of exercise and talk to your doctor about your risk factors.
To keep up with our latest information, be sure to follow us on Facebook and Instagram and check our blog page often.
Written by S. Campbell for Access Health Care Physicians, LLC.


