The significance of urologists in the landscape of medical disciplines sometimes needs to be recognized until a specific issue develops. However, the value of urologists in sustaining general health and well-being cannot be emphasized enough.
What is Urology?
Urology is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract and male reproductive organ problems. The kidneys, bladder, ureters, urethra, and male reproductive organs such as the prostate and testes are all included.
Urologists get considerable study and training, beginning with medical school and continuing with a urology residency. Their knowledge spans a wide spectrum of problems, making them ideally prepared to address a variety of urological issues.
The Scope of Urological Expertise
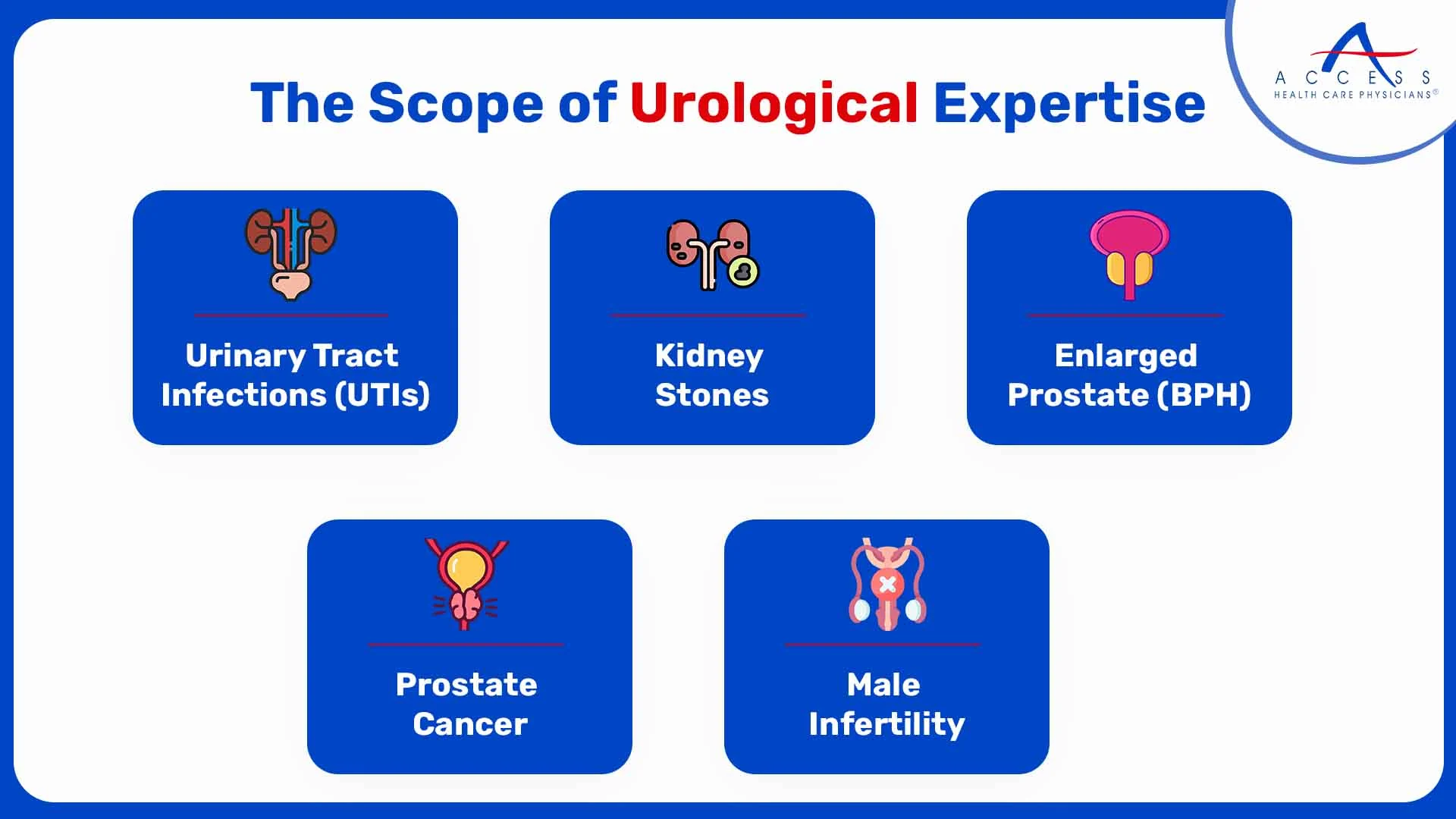
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
Urologists are frequently consulted for persistent or severe urinary tract infections. They are capable of identifying underlying problems, prescribing suitable treatments, and providing prevention advice.
- Kidney Stones:
Kidney stones are one of the most prevalent ailments that urologists treat. These unpleasant mineral deposits can accumulate in the kidneys and cause severe pain. To manage and remove kidney stones, urologists use a variety of approaches, including minimally invasive procedures.
- Enlarged Prostate (BPH):
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common disorder that causes an enlarged prostate in older men. Urologists can treat symptoms and enhance quality of life with medication and surgical procedures.
- Prostate Cancer:
Urologists play an essential role in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer. They can recommend screenings, such as PSA tests, and can walk patients through the various treatment options, which may include surgery, radiation, or active monitoring.
- Male Infertility:
Urologists who specialize in reproductive medicine can examine and treat male infertility difficulties for couples experiencing infertility. This could include treating difficulties with sperm production, quality, and delivery.
Signs You Need to See a Urologist
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort:
Chronic pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or genitals may suggest a urological problem. A urologist can assist in determining the reason and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
- Changes in Urinary Function:
Any changes in urinary patterns, such as increased frequency, urgency, pain during urination, or blood in the urine, should be evaluated by a urologist. These symptoms could be caused by several illnesses, including infections or bladder problems.
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED):
While ED can be caused by a variety of factors, including psychological ones, urologists can evaluate and treat physical causes such as vascular abnormalities or hormonal imbalances. Seeking their advice can lead to effective ED treatments.
- Concerns About Prostate Health:
Men who have symptoms of prostate health, such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, or raised PSA values, should see a urologist. Proactive prostate health management is critical for early detection and treatment of any problems.
- Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
Frequent UTIs could indicate an underlying urinary system disease. Urologists can look into the underlying reason and propose measures to prevent the recurrence of infections.
Urologists and Preventive Care
- Screening and Early Detection:
Regular urological check-ups can help in the early diagnosis of any urological problems. Prostate cancer screening, in particular, is an important feature of preventative urological therapy.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
Urologists can advise patients on lifestyle modifications that will improve their urological health. This could include dietary advice, exercise, and routines that can help prevent kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and other problems.
- Proactive Management of Chronic Conditions:
Urologists play an important role in controlling symptoms, preventing complications, and increasing the overall quality of life for people with urological disorders such as chronic kidney disease or interstitial cystitis.
Urology for Women
While urologists have traditionally been identified with male reproductive and urinary health, they also specialize in female urology. They treat urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and interstitial cystitis, and offer comprehensive care to both men and women.
Urologists and gynecologists work together to treat urine incontinence and pelvic floor diseases in women. These disorders can have a substantial influence on a woman's quality of life, and urologists provide a variety of treatment options, including physical therapy and surgical therapies.
To summarise, the function of urologists in maintaining urological health is critical. Urologists make a substantial contribution to general well-being, from disease prevention and early identification to chronic disease management.
Connect with the expert physicians at Access Health Care Physicians for regular check-ups, proactive lifestyle changes, and timely consultations
Frequently Asked Questions
Any kidney or prostate-related diseases can be diagnosed by a urologist.
UTIs, chronic kidney disease, and kidney stones are common urology issues.
The most common urine test is a urinalysis, which is performed to look for germs, foreign objects, and blood cells. This test may also help in the diagnosis of urinary tract infections, diabetes, and the early stages of illness.