Caffeine, which occurs naturally in coffee, tea, and cocoa and is added to many popular beverages and pharmaceuticals, is profoundly engrained in our everyday lives. Caffeine is a stimulant of the central nervous system that is consumed by millions of people worldwide every day. Most people are heavily reliant on their daily morning cup of joe to get through the day.
While caffeine can deliver a much-needed energy boost and increase alertness, many people are concerned about its possible influence on heart health. Tea and coffee are extremely healthy beverages however, according to studies, caffeine is safe for most people to consume in low to moderate quantities only.
Excessive caffeine consumption can have unpleasant and hazardous adverse effects.
How Does Caffeine Work in the Body?
Before diving into caffeine's effects on the heart, it's important to understand how caffeine functions in the body.
Caffeine enters your system quickly and travels to your brain when you consume it, acting as an adenosine receptor antagonist. This means that it inhibits the neurotransmitter adenosine, which promotes relaxation and sleepiness.
Caffeine improves alertness, mood, and cognitive performance by reducing the effects of adenosine.
Caffeine additionally stimulates the production of adrenaline, the "fight-or-flight" hormone, which boosts heart rate, blood pressure, and heart muscle contractility. These effects are responsible for the reported improvement in energy and alertness following caffeine consumption.
How much caffeine is too much?
According to the United States FDA, 400 milligrams of caffeine per day is typically safe for most people. That's roughly the caffeine content of four cups of brewed coffee, ten cans of soda, or two energy-shot beverages.
Caffeine intoxication can occur at doses of 500 milligrams or more. Common symptoms of caffeine intoxication are:
-
Anxiety
-
Panic attacks
-
Increased gastric acid
-
Bowel irritability
-
Sleep deprivation or insomnia
Short-Term Effects of Caffeine on the Heart
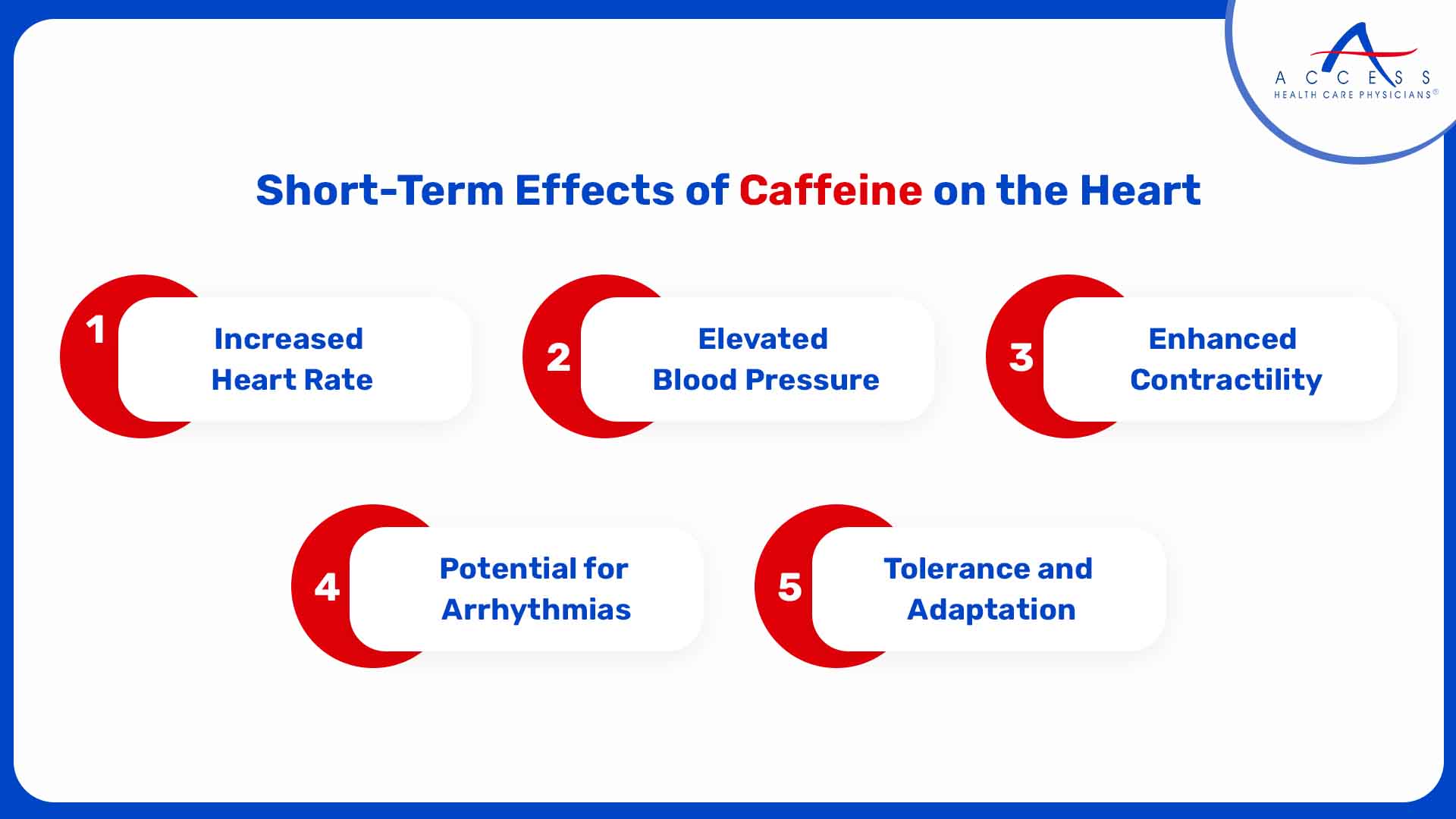
1. Increased Heart Rate:
One of the most noticeable effects of caffeine is an increase in heart rate. This is due to caffeine's capacity to boost adrenaline release. The change is minor and transient for most people, but it can be more evident in those who are caffeine-sensitive or consume high amounts.
2. Elevated Blood Pressure:
Caffeine is known to lead to a temporary, yet significant, increase in blood pressure. While this impact is usually minor and short-lived, it can be concerning for people who have high blood pressure or other cardiovascular issues.
3. Enhanced Contractility:
Caffeine has an effect on the heart by increasing the force of cardiac contractions. This can temporarily increase cardiac output, which may be advantageous during strenuous physical activity.
4. Potential for Arrhythmias:
Caffeine use may cause abnormal heart rhythms or heart palpitations (a sense of a quick, powerful, or irregular heartbeat) in some people. However, these effects are typically observed in caffeine-sensitive individuals or those who ingest excessive doses of caffeine.
5. Tolerance and Adaptation:
Over time, regular caffeine consumers often develop tolerance to its acute effects on the heart, meaning they experience reduced heart rate and blood pressure responses to the same amount of caffeine. This tolerance can vary from individual to individual.
Long-Term Effects of Caffeine on Heart Health
While moderate caffeine consumption is generally considered safe for most individuals, the long-term effects of caffeine on heart health are a topic of ongoing research.
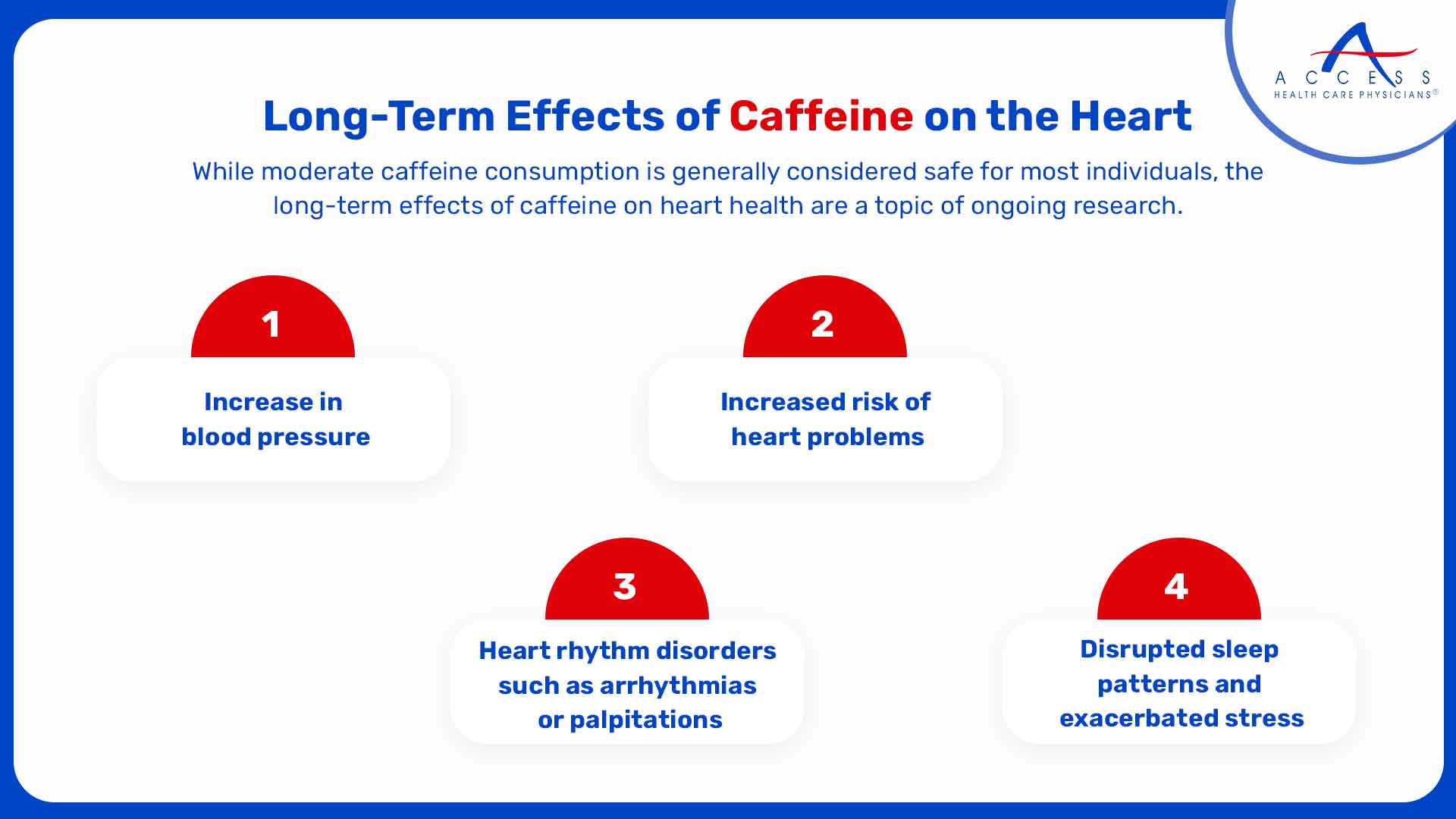
Here are some key considerations:
-
Increase in blood pressure
-
Increased risk of heart problems
-
Heart rhythm disorders such as arrhythmias or palpitations
-
Disrupted sleep patterns and exacerbated stress
Individual Variability in Response to Caffeine
It's essential to recognize that individual responses to caffeine can vary significantly. Factors that influence how caffeine affects the heart include
-
Genetics
-
Tolerance over time
-
Sensitivity levels
-
Underlying health conditions such as high blood pressure, arrhythmias, or anxiety disorders
Caffeine and Specific Heart Conditions
Caffeine enters your bloodstream from the stomach and small intestine and begins to stimulate your central nervous system the moment you take your first sip of coffee. Caffeine stimulates the receptors in the cells of your heart, increasing your heart rate.
As your heart rate increases — by around three beats per minute — so does your blood flow. Caffeine can cause an increase in your heart rate in as little as 15 minutes and last for nearly six hours.
While moderate caffeine consumption is generally considered safe for most individuals, people with specific heart conditions should exercise caution or consult their primary care physician regarding caffeine intake.
Here are some considerations for individuals with particular heart conditions:
-
High Blood Pressure
-
Arrhythmias
-
Cardiac Medications
-
Heart Failure
Guidelines for Safe Caffeine Consumption
For most individuals, moderate caffeine consumption is considered safe and may even offer some potential health benefits.
The following guidelines can help you make informed decisions about your caffeine intake:
-
Moderation is key. Consume caffeine in moderate quantities, depending on how your body reacts to it.
-
Be aware of your individual tolerance and sensitivity to caffeine.
-
Avoid consuming caffeine too late in the day, as it can interfere with sleep patterns.
-
Balance your caffeine intake with adequate hydration. Consume the recommended amount of water or try infused water to make it more enjoyable.
-
If you notice any adverse reactions or unusual symptoms related to your heart, consult a healthcare professional instantly.
Benefits of Moderate Caffeine Consumption
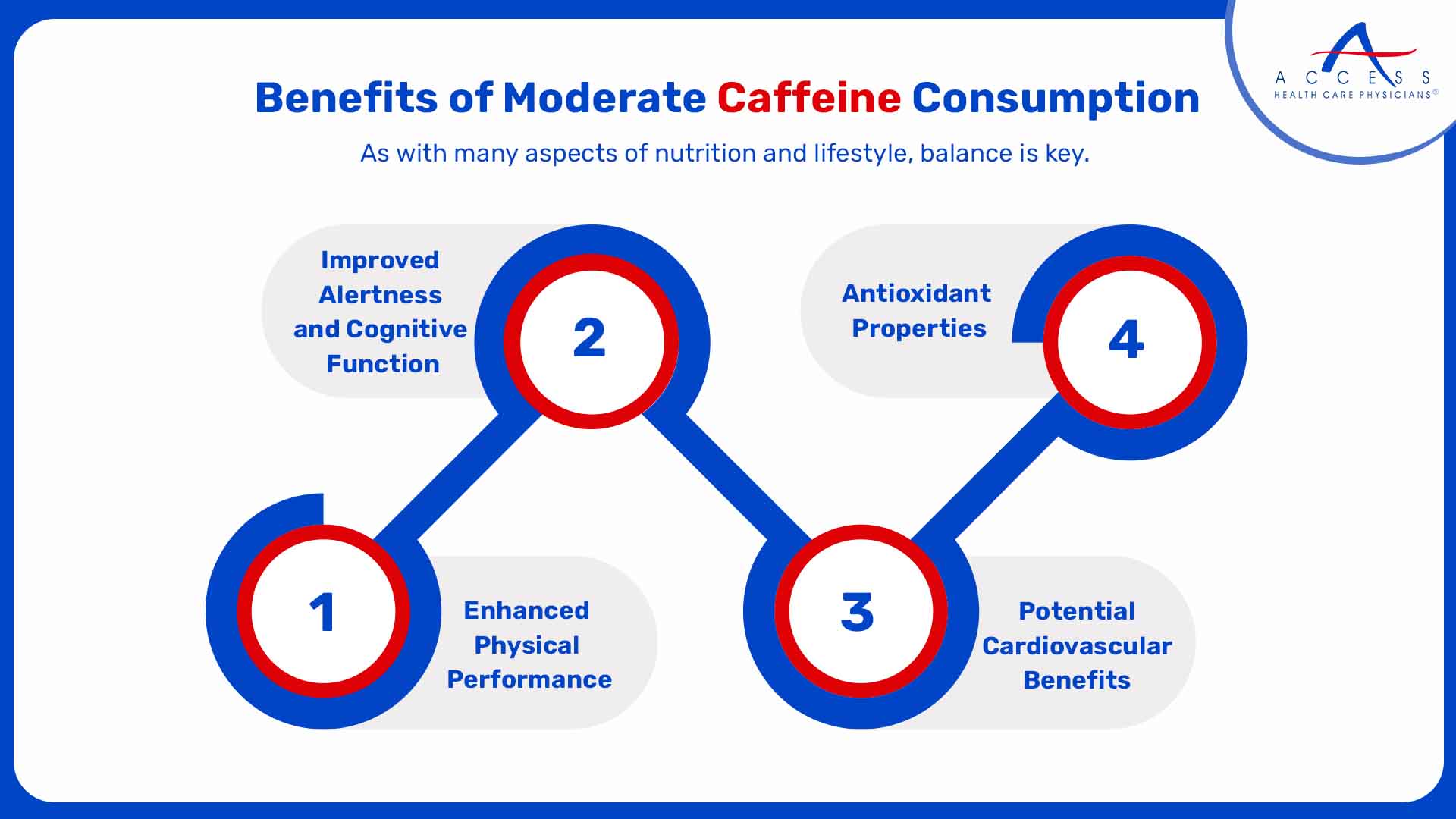
-
Improved Alertness and Cognitive Function
-
Enhanced Physical Performance
-
Antioxidant Properties
-
Potential Cardiovascular Benefits
As with many aspects of nutrition and lifestyle, balance is key. While caffeine might temporarily raise heart rate and blood pressure, moderate use is typically regarded as safe for most healthy people.
Individual responses to caffeine vary, therefore patients with certain heart issues should exercise caution and check with their healthcare providers about their caffeine use. Contact Access Health Care Physicians to book an appointment at the earliest.
The relationship between caffeine and heart health is complex, and individual choices should be informed by the best available evidence and tailored to personal health circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Effects of caffeine include increased heart rate, breathing, and more mental alertness and physical energy.
Yes, caffeine can have a short-lasting but dramatic increase in blood pressure.
An excessive amount of caffeine drinks can cause harmful effects on your heart.


