Many of us are all quite familiar with feeling cognitively cloudy and physically lethargic. Our fast-paced lifestyles may make us feel productive, but when pushed too far, our pace can jeopardize our health, vitality, and even spiritual well-being.
Individuals frequently blur the lines between relaxation and sleep in our fast-paced environment, when time is a valued commodity.
While they may appear to be similar at first look and may seem to have the same intent, they each have distinct meanings and play specific functions in our overall health and well-being.
What is the difference between Rest and Sleep?
Though they are closely connected, rest and sleep serve different objectives and involve separate physiological processes.
Rest is a state of relaxation and leisure in which the body and mind are less active and stressed.
It includes a wide range of activities, from sitting quietly to indulging in light, non-vigorous activities such as reading, meditating, or listening to soothing music. In comparison to wakefulness, rest is distinguished by a reduced level of physical and mental exertion.
Sleep, on the other hand, is a naturally occurring state of unconsciousness and inactivity characterized mostly by diminished receptivity to environmental stimuli.
It is a critical aspect of the sleep-wake cycle for the body's restoration, repair, and cognitive function. Sleep takes place in several stages, each of which serves a specialized purpose in retaining well-being.
Physiological Aspects of Rest and Sleep
To better understand the differences between rest and sleep, let's explore their physiological aspects:
a. Rest
-
During rest, the body stays awake, but at a reduced degree of activity.
-
While the brain remains active, people can experience relaxation, reduced tension, and an overall sensation of peace.
-
Rest can occur both in wakefulness and during sleep when transitioning between sleep stages.
b. Sleep
-
Sleep involves distinct stages, including non-REM (rapid eye movement) and REM sleep.
-
Non-REM sleep consists of four stages, with each stage serving a specific purpose in physical and mental restoration.
-
REM sleep is associated with vivid dreams and plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional regulation.
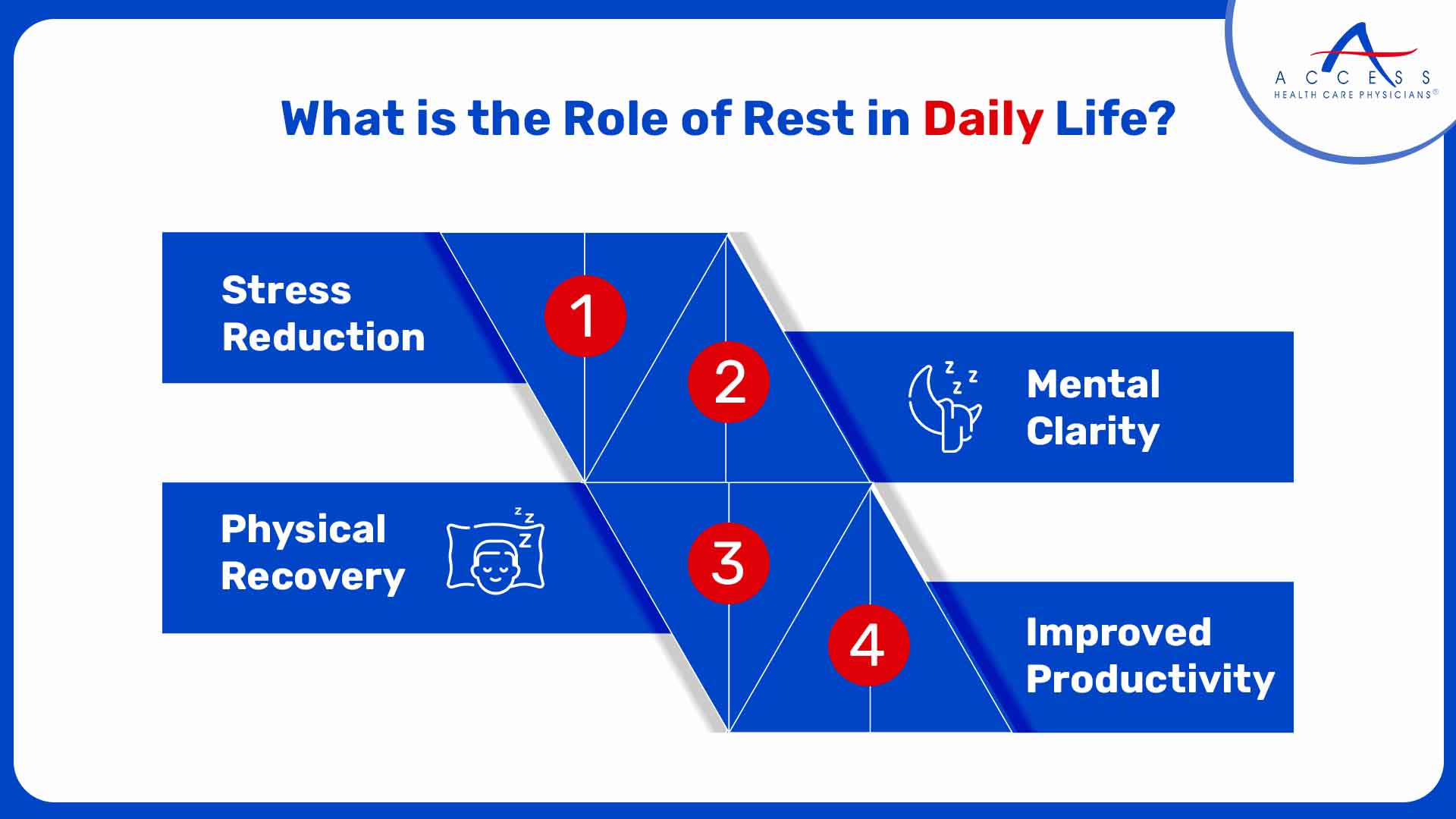
What is the Role of Rest in Daily Life?
Rest plays a significant role in our daily lives and has several important functions, such as:
-
Stress Reduction - Taking regular breaks to engage in activities that encourage relaxation and help your body recover has been shown to reduce stress levels.
-
Mental Clarity - Resting has proven to enhance mental clarity and improve decision-making as it allows the mind to recharge. Rest helps tremendously with brain fog.
-
Physical Recovery - If your body has been under constant stress, periods of rest can help muscle recovery and heal minor injuries as well.
-
Improved Productivity - Incorporating rest breaks into work or study routines is known to boost productivity as it prevents burnout.
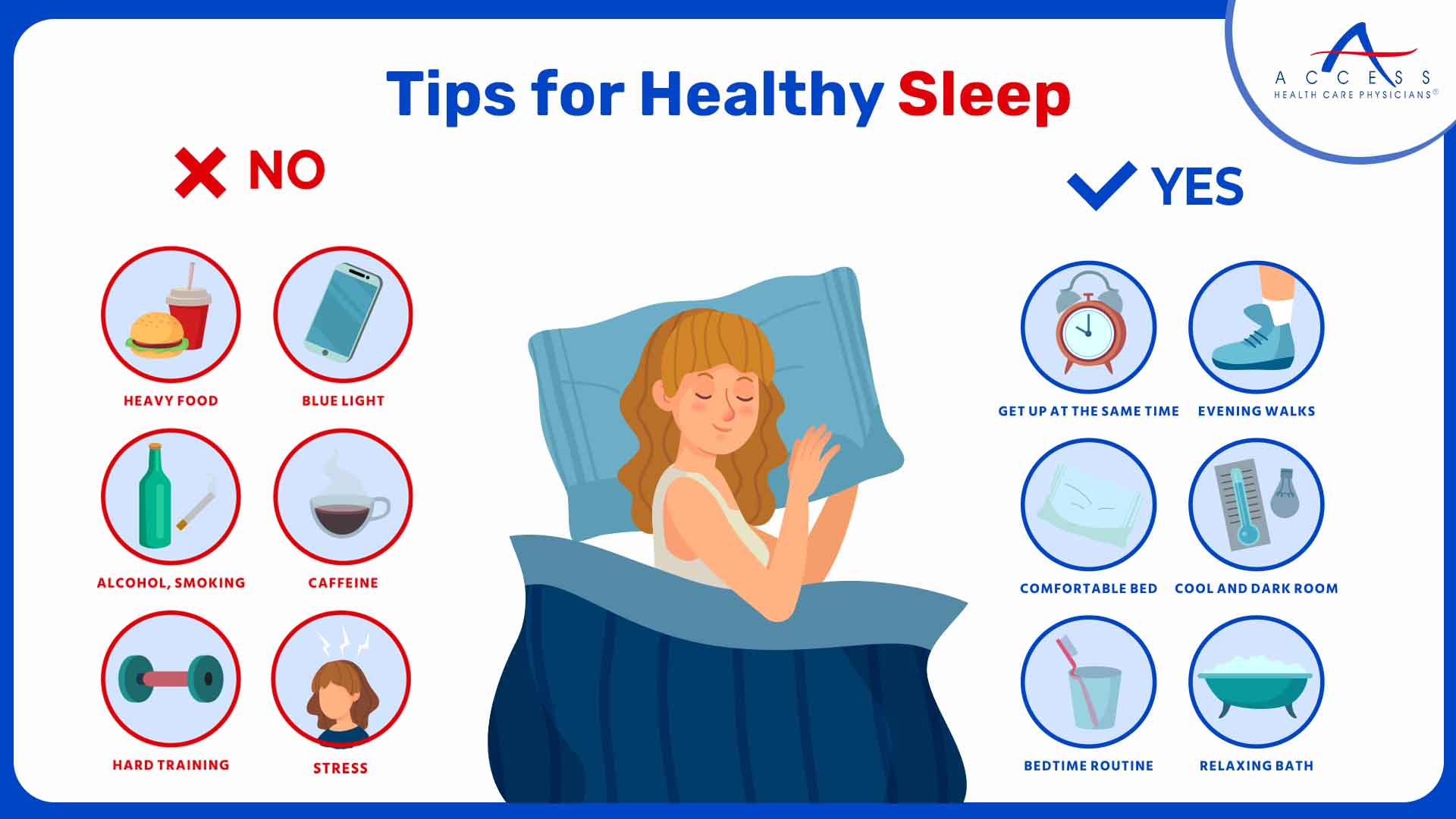
Tips to incorporate Rest into your life
-
Being mindful and taking moments of gratitude
-
Take yourself out of stressful or anxious situations for a brief period of time
-
Plan a short getaway
-
Take a short nap
-
Avoid caffeine or anything that will make your nerves hyperactive
What is The Sleep-Wake Cycle?
The circadian rhythm, often known as the sleep-wake cycle, is a natural, 24-hour biological pattern that regulates our sleep and wake cycles.
External factors such as light and temperature, as well as internal biological processes influence it. The sleep-wake cycle is crucial in determining when we are most attentive and awake, as well as when we have a strong need to sleep.
Night shifts at work, inconsistent sleep cycles, and late exposure to artificial light can all disrupt the circadian rhythm. Such disruptions might result in sleep issues, exhaustion, mood swings, and higher health risks.
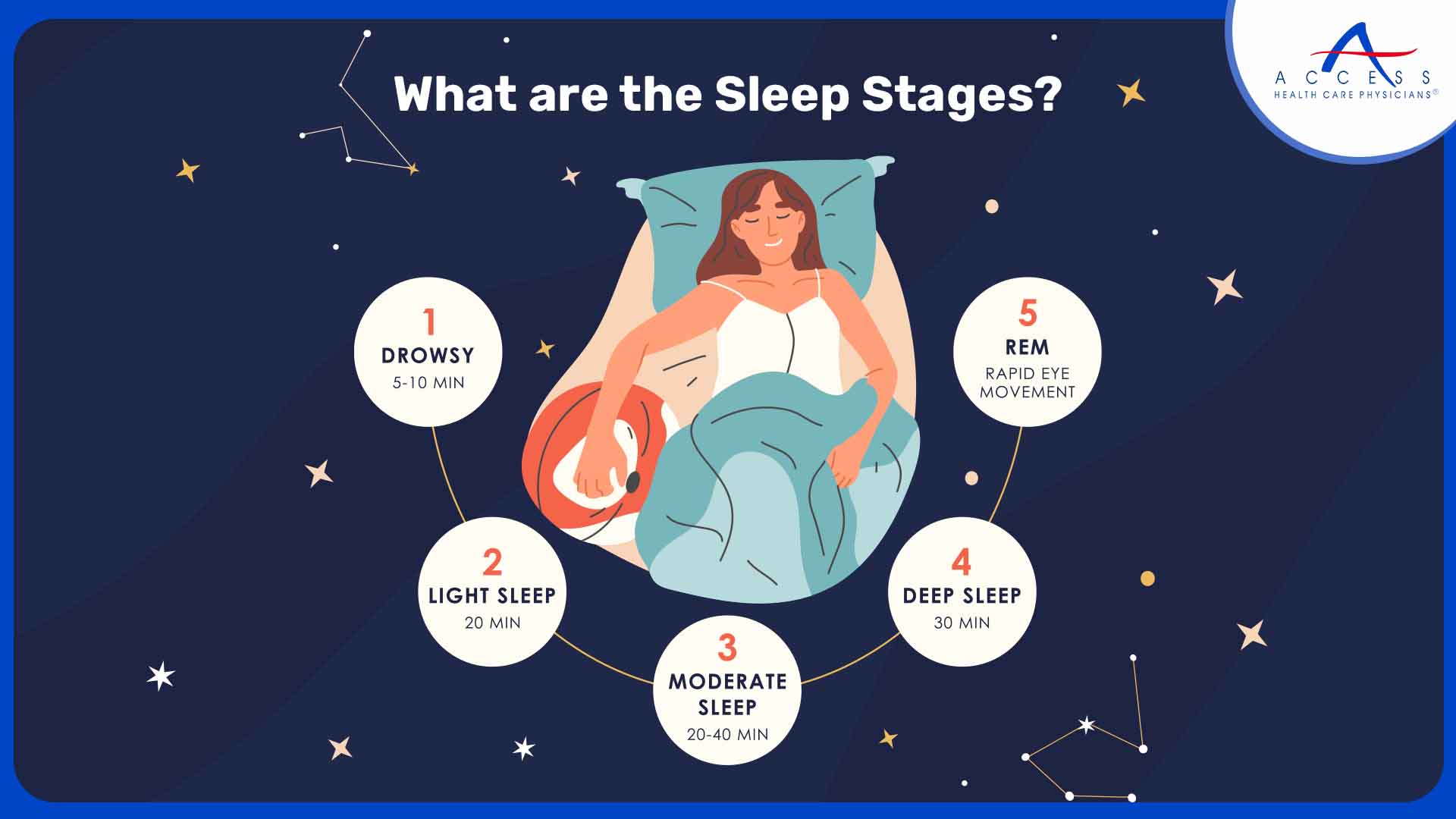
What are the Sleep Stages?
The sleep-wake cycle, which normally lasts 24 hours, consists of alternating stages of sleep and wakefulness. These stages have a consistent structure and include periods of enhanced and decreasing awareness.
Non-REM sleep is divided into four stages, each of which serves a different function such as tissue repair and growth hormone production.
Later in the cycle, REM sleep helps cognitive processing, emotional regulation, and memory consolidation.
While the average adult requires 7-9 hours of sleep each night, there are individual differences in circadian rhythm. Some people are "night owls" who are more attentive and active in the evening, while others are "morning larks" who are most alert in the morning.
Individual differences are partly determined by genetics, but they can also be impacted by lifestyle and other environmental factors.
Health Benefits of Sleep
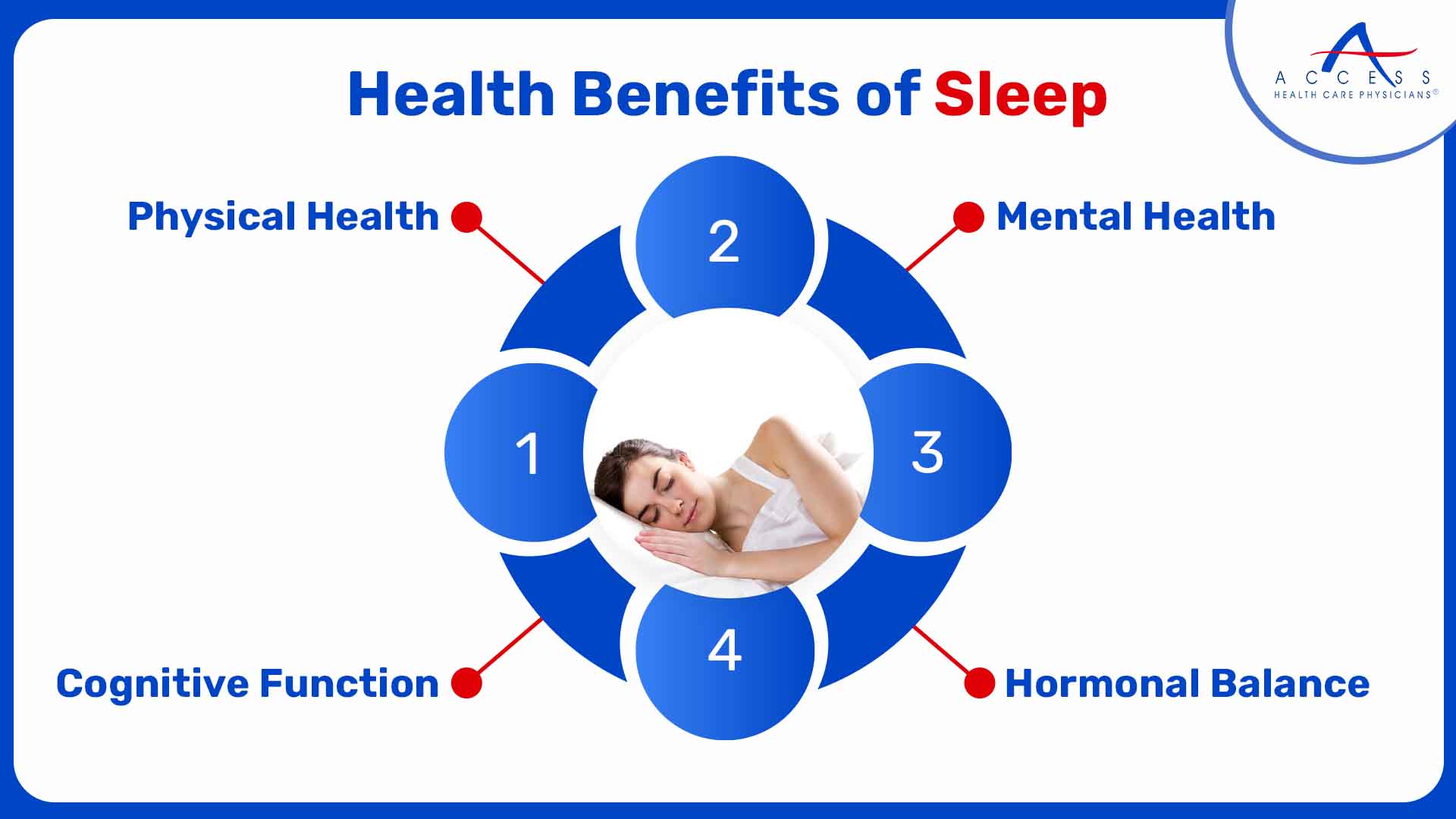
1. Physical Health:
Adequate sleep is essential for physical health, as it promotes the strengthening of the immune system and helps in tissue repair and maintenance. Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of illnesses like obesity, diabetes, chronic stress and heart disease.
2. Mental Health:
Sleep is essential for mood and emotion regulation. Sleep deprivation has been connected to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
3. Cognitive Function:
Lack of sleep can impair cognitive capacities, resulting in lower productivity and poor decision-making.
4. Hormonal Balance:
Sleep is integrally linked to hormone regulation, including growth hormone, cortisol, and insulin release. Sleep deprivation can upset hormone balance and cause issues with metabolism.
Rest and Sleep: Finding the Right Balance
Achieving the right balance between rest and sleep is crucial for overall well-being:
-
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep every night to support physical and mental health.
-
Maintain a regular healthy sleep schedule to regulate your circadian rhythm.
-
Incorporate short rest breaks during the day to recharge your mind and reduce stress.
-
Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing to enhance restfulness.
-
Limit exposure to screens and stimulating activities before bedtime to promote better sleep quality.
-
Avoid pushing yourself to the point of exhaustion, as this can lead to burnout and poor sleep.
In the midst of modern life's hustle and bustle, it's easy to overlook the value of relaxation and sleep. Recognizing the differences between these two states, as well as knowing their physiological elements and health advantages, is critical for general well-being.
Connect with a physician at Access Health Care Physicians to learn more about sleep and rest. By finding the right balance between rest and sleep, you can unlock the key to a healthier, more productive, and fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Resting is a state in which our bodies relax after a stressful routine but our mind is still active. Sleep, on the other hand, is a type of altered conscious state in which the body shuts down all physical and mental functions.
It does not. While resting makes us feel relaxed, it cannot substitute the need for sleep.
A balance of both rest and sleep is required for maintaining one’s well-being and health.
You can partake in various relaxing activities such as meditation, taking breaks to do nothing or intentionally resting.


